Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attack

With the advancement of science and technology, not only network equipment has grown significantly, but hackers and cyberattacks have also developed with these advances. Therefore, to combat threats and security protocols have been created to protect information and documents from hacking and damage.
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks are carried out for several reasons. One of the main goals is to steal sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, or other personal data.
In this article, we are going to introduce Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attack to you completely and explain its features and operation.
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attack:
A Man-in-the-Middle attack is a type of cyberattack where a hacker secretly intercepts, relays, or even alters the communication between two parties (like you and a website) without either party knowing. Attackers may also use this method to bypass authentication systems, allowing them to access protected accounts or systems.
Additionally, they might inject malicious content into communications to spread malware or manipulate data. In some cases, MITM attacks are used to secretly spy on corporate or governmental targets to gather intelligence.
These attacks can happen through various common methods. For example, attackers may create fake Wi-Fi hotspots to lure victims into connecting, making it easy to intercept their data.
Another method is DNS spoofing, where users are redirected to fake websites that look legitimate. HTTPS spoofing tricks users into visiting an insecure version of a secure site, making it easier to intercept or alter the data.
Lastly, session hijacking involves taking control of a user’s session after they have logged in, allowing the attacker to act as if they are the real user.
Imagine you’re talking to a friend on the phone.
Now imagine someone else is silently listening to your call and maybe even changing what you hear or say. That’s what a MITM attack is but in the digital world.
Features of Man-in-the-Middle Attacks:
- Eavesdropping:
The attacker silently listens to the conversation and collects data (like login info, credit card numbers, etc.). - Data Manipulation:
The attacker can modify the data being sent between the two parties (e.g., changing the amount of money in a bank transfer). - Impersonation (Spoofing):
The attacker pretends to be one of the parties to fool the other (like pretending to be a bank’s website). - Usually Stealthy:
Victims don’t know it’s happening because everything seems normal. - Real-Time:
It happens live, as you’re using the internet or network.
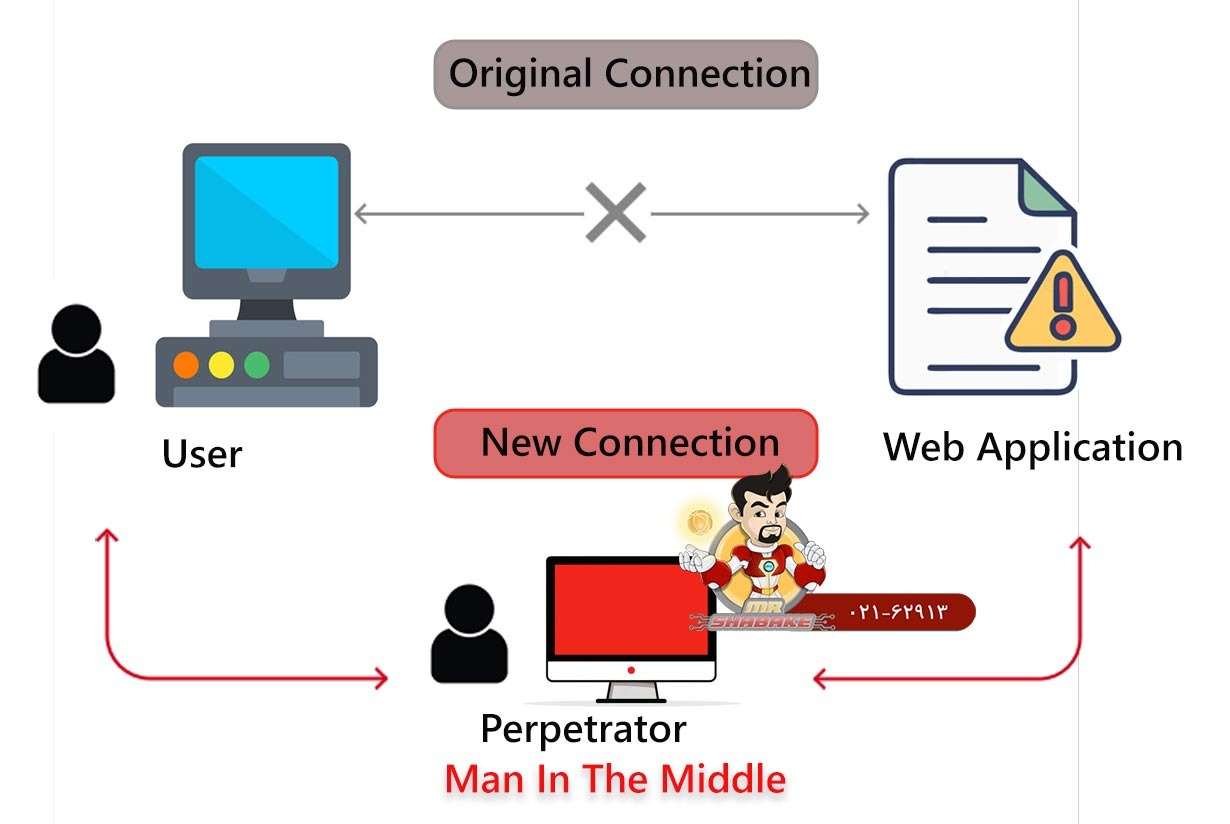
Why and how does Man-in-the-Middle happen?
Why it’s done?
- Steal sensitive information (passwords, credit card info, personal data)
- Bypass authentication
- Inject malicious content
- Spy on targets (corporate or government)
How it happens (common methods)?
- Unsecured Wi-Fi networks: Hackers set up fake Wi-Fi hotspots.
- DNS spoofing: Redirect users to fake websites.
- HTTPS spoofing: Tricking you into visiting a non-secure version of a secure site.
- Session hijacking: Taking control of a user’s session (e.g., after login).
How to protect yourself from MITM attacks?
To protect yourself from Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks, it’s important to focus on securing your communication, verifying websites and connections, and being cautious on public networks.
Using secure technologies, staying alert, and keeping your devices updated can greatly reduce your risk. Whether you’re an everyday internet user or managing a network, these steps are crucial for preventing unauthorized interception and manipulation of data.
- Always use HTTPS (look for the lock icon in your browser).
- Avoid public or untrusted Wi-Fi for sensitive transactions.
- Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) to encrypt your data.
- Keep your system and apps up to date.
- Use strong passwords and two-factor authentication.
Read more: Internet Control Message protocol (ICMP)
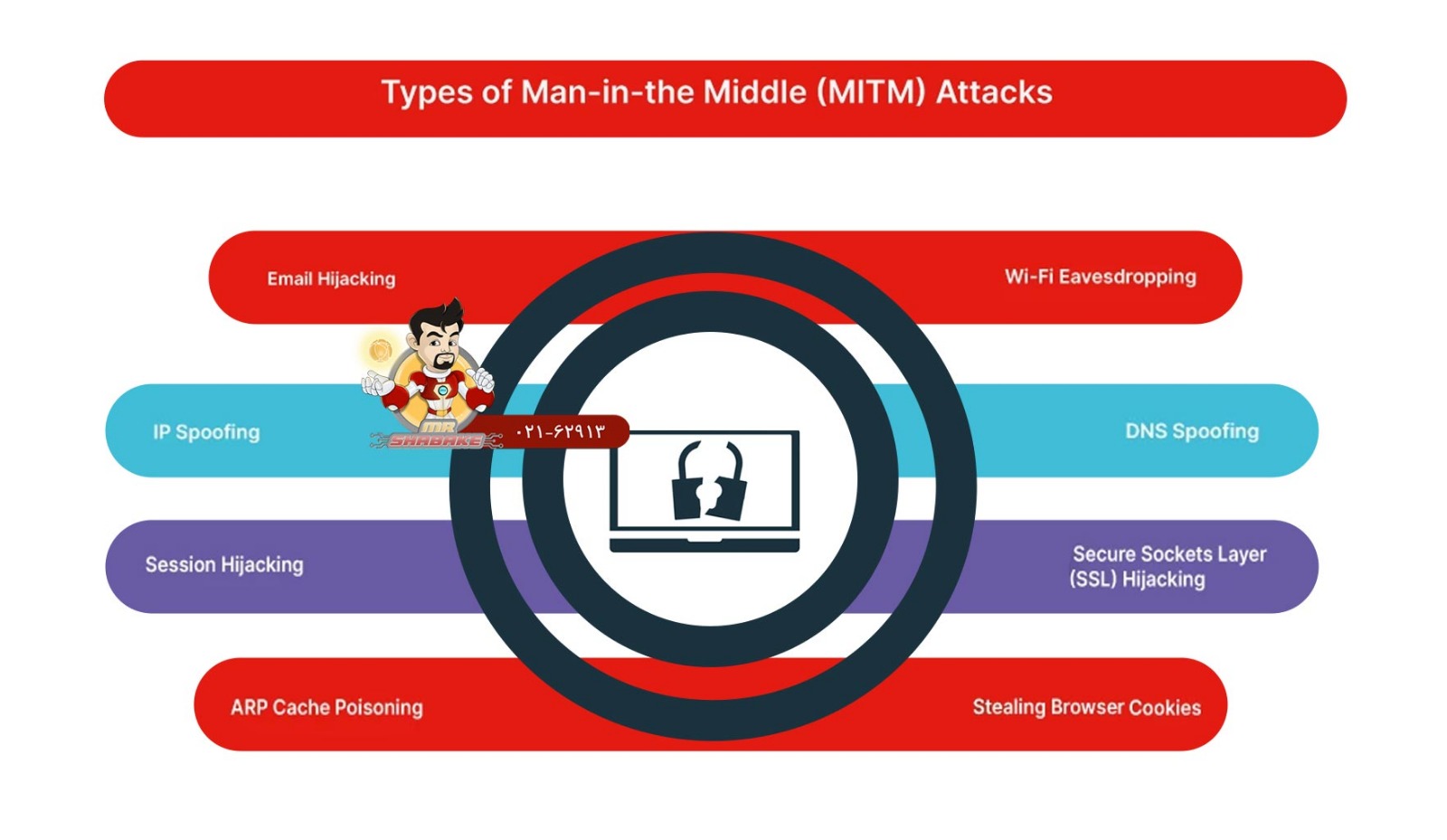
Types of Man-in-the-Middle Attack:
1. Packet Sniffing (Eavesdropping)
- Goal: To secretly listen to unencrypted data.
- How: The attacker uses tools like Wireshark to capture network traffic on unsecured networks (e.g., public Wi-Fi).
- Targets: Login credentials, emails, messages.
- Defense: Use HTTPS, VPNs, or encrypted apps.
2. HTTPS Spoofing / SSL Stripping
- Goal: Downgrade HTTPS to HTTP to read or modify traffic.
- How: The attacker forces the victim to connect over HTTP, making it easier to intercept data.
- Example Tool: sslstrip
- Defense: Enforce HTTPS (HSTS), browser security warnings, VPN.
3. DNS Spoofing (DNS Cache Poisoning)
- Goal: Redirect the victim to a malicious site.
- How: Attacker alters DNS responses to send users to a fake server (e.g., fakebank.com instead of realbank.com).
- Defense: Use DNSSEC, trusted DNS resolvers, VPN.
4. ARP Spoofing (Address Resolution Protocol)
- Goal: Intercept LAN traffic by associating the attacker’s MAC address with another IP.
- How: The attacker sends fake ARP messages to the LAN.
- Result: Victim unknowingly sends data to the attacker.
- Defense: Static ARP tables, ARP monitoring tools.
5. Wi-Fi Evil Twin Attack
- Goal: Trick victims into connecting to a fake Wi-Fi network.
- How: The attacker sets up a rogue Wi-Fi access point with the same name (SSID) as a trusted one.
- Defense: Avoid open Wi-Fi, verify SSL certificates, use VPN.
6. Session Hijacking
- Goal: Take over a user’s session with a website.
- How: Steal session cookies via sniffing or XSS.
- Result: Attacker gains unauthorized access (e.g., logged-in accounts).
- Defense: HTTPS, secure cookies, regenerating session IDs.
7. Man-in-the-Browser (MitB)
- Goal: Modify browser transactions.
- How: Malware (like a trojan) is injected into the browser.
- Used For: Banking fraud, data theft.
- Defense: Antivirus, browser hardening, secure plugins.
Man-in-the-Middle Attack Progression (Steps):
Intercepting the Communication: The attacker first needs to position themselves between the two communicating parties (e.g., you and a website). This can happen by:
- Creating a fake Wi-Fi hotspot (evil twin attack)
- ARP spoofing in a local network
- DNS spoofing to redirect users
- Using malware installed on the victim’s device
Monitoring or Modifying Data: Once in the middle, the attacker starts to monitor, capture, or alter the data being transmitted.
- They might steal login info, emails, credit card details, etc.
- Or they might inject false data or malware into the communication
Impersonation (Optional): The attacker may also impersonate one or both parties.
- For example, they could pretend to be a bank website when you’re trying to log in.
- The victim thinks they’re talking to the real site, but it’s actually the attacker.
Exfiltration of Data: The stolen information (like passwords, banking info, or private messages) is then collected and possibly sent to another system or server controlled by the attacker.
Covering Tracks (Optional): Sophisticated attackers may try to hide their activity, making it harder to detect the MITM attack. They might encrypt their stolen data, clear logs, or restore original communication afterward.
Man-in-the-Middle Attack Prevention Tips:
- Use HTTPS only: Always make sure websites have HTTPS in the URL (not just HTTP). Look for the lock icon in your browser.
- Avoid public Wi-Fi: Don’t access sensitive accounts (like banking) on public or unsecured Wi-Fi. Use your mobile data or a trusted network instead.
- Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network): A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, making it unreadable to attackers, even on public networks.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): Adding 2FA makes it harder for attackers to access your accounts even if they steal your password.
- Keep software and devices updated: Updates fix security vulnerabilities that attackers often use in MITM attacks.
- Verify website certificates: On suspicious websites, click the lock icon to view the SSL certificate details and make sure it’s valid and issued by a trusted authority.
- Use strong, unique passwords: This helps protect your accounts in case one of your credentials gets exposed.
- Be cautious of phishing links: Attackers may send fake links that lead to spoofed websites to perform a MITM attack.
Using Imperva to Protect Against Man-in-the-Middle Attacks:
Imperva offers a range of security solutions that help prevent MITM attacks by protecting data in transit, securing web applications, and monitoring traffic for suspicious behavior.
It focuses on preventing unauthorized access, encrypting data, and detecting anomalies in real-time. By using Imperva’s tools, organizations can strengthen their defenses and ensure that sensitive communications are secure from interception or tampering.
Key Imperva Features for MITM Protection:
- Web Application Firewall (WAF):
Imperva’s WAF protects websites and applications from malicious traffic, including MITM-style data injection or manipulation attacks. - TLS/SSL Enforcement:
It enforces strong encryption protocols (HTTPS) for all data in transit, preventing attackers from reading or altering the information. - Bot Protection:
Detects and blocks malicious bots that might be used in automated MITM scenarios, such as session hijacking. - DDoS Protection:
While not directly related to MITM, DDoS protection helps prevent attackers from overwhelming and distracting a network before launching a MITM attack. - Traffic Monitoring and Anomaly Detection:
Imperva monitors all incoming and outgoing traffic to detect unusual patterns that may suggest a MITM attack is taking place.
- Secure CDN (Content Delivery Network):
Ensures that all data is securely distributed and protected against interception during delivery.
Conclusion:
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks are a serious cybersecurity threat where attackers secretly intercept and possibly alter communication between two parties. These attacks can lead to the theft of sensitive data, such as passwords, personal information, or financial details.
MITM attacks often go unnoticed and can occur through unsecured networks, fake websites, or session hijacking. Preventing them requires strong encryption (like HTTPS), secure network practices, the use of VPNs, regular software updates, and tools like Imperva to monitor and protect traffic.
In today’s digital world, understanding and defending against MITM attacks is essential for both individuals and organizations to ensure privacy, trust, and data security.





