What is a server power supply

Most of computer and servers use DC, not AC, which is the type of power that comes from wall outlet. So the power supply is a hardware that power all parts of a server. The primary aim of power supply is converting alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). In this article, we will survey all about server power supply.
A power supply helps to server for working better. Server is one of the most important part of network equipment, if this part works well, other members of network equipment such as Network switch, Network router, Network Module and more, make a useful network.
What is a server power supply:
Despite the name, server power supply do not supply systems with power, instead they convert it. Specifically, a server power supply converts the alternating high voltage current (AC) into direct current (DC), and they also regulate the DC output voltage to the fine tolerances required for modern computing components.
Most power supplies are switched-mode (SMPS), which has both efficiency advantages and makes designing for multiple voltage inputs easier. This means that most server power supplies can operate in different countries where the power input might change. In the UK, the voltage is 240V 50Hz, whereas in the USA the voltage is 120V 60Hz, and in Australia it is 230V 50Hz.
When do we need a server power supply:
Power supply is one of the most important part of a server, without it your IT infrastructure doesn’t work. So it’s really normal that most systems include a power supply upon purchase. Although there is an alternative to the power supply that can be used in some instances.
By choosing Power over Ethernet (PoE), electrical power can be carried within network cables without being tethered to an electrical outlet. This is ideal for systems that need more flexibility; PoE can provide wireless access points to wherever that is most convenient, and less space is taken up by wiring.
How to choose a power supply for server:
The choice of a power supply should take into account your existing parts; it must match in terms of size and power. The more complex your system, the higher the demands placed on the power supply.
Although the manufacturer is important, it’s not the sole determining factor, as every brand produces products of varying quality. It’s essential to review professional feedback on specific product lines and consider the manufacturing year. So follow these orders:
Firstly, when choosing a power supply unit, it is important to make sure it is compatible with the form factor of your server case and motherboard. This will ensure it fits within your server.
Then, wattage is an important factor to consider. The higher the wattage rating, the more power the unit can provide to your system, meaning that you need to evaluate how much power your components require to run effectively. For instance, if the components in your system require 600V, it would be ideal to buy a 1200V power supply unit, as most power supplies have the highest efficiency at ≈50% load. This also allows for room to expand your system with further components if needed.
Finally, when replacing or upgrading a PC power supply unit, it is important to take brands into consideration. Popular brands for power supplies include Corsair, Antec, EVGA and Seasonic. The choice often comes down to personal preference, compatibility with your system, and what you are using the power supply for (e.g. gaming, a small or large business, or personal use). One piece of advice is to look out for an 80 Plus Platinum rating, as this has great energy efficiency and can minimise power costs.
In addition, among server power supplies, models with redundant units are preferable. Specialized power supplies with “two in one” redundancy allow you to replace one part of the unit quickly and without complications. Cold redundancy function helps save electricity when the computer is in standby mode.
Redundant power supplies must activate rapidly, transitioning from standby to full operation. A computer bus that continuously monitors system activity and detects errors can prove invaluable in maintaining server stability. Remember, choosing the right power supply for your server is essential for maintaining its reliability and performance.
Does a server need more than one power supply:
In short, a server will always need at least two power supplies. There are different modes of operation for this, depending on how much redundancy you need in your system. One option is to have a fully redundant power supply system, which means that one power supply is always switched off and there is an emergency fall back in case of downtime.
The other option is to have shared power supplies, where both are on at the same time and share the workload. At Techbuyer, we suggested that you provide double the amount of wattage than you actually need, to ensure optimum uptime.
For maximum redundancy, it is also a good idea to have an Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS), which enables your computer to run for a limited time if power is lost.
There are three types: online, offline and line-interactive. Online Uninterrupted Power Supplies ensure the quality of power remains constant, whereas offline UPSs start running when power is lost and there will be a slight delay when it takes over. Line-interactive is a combination of the two and provides more power protection thanks to its line conditioning.
Read more: What is Cisco network module
Regular VS server power supplies:
Maybe this is a question that make you confuse, the first distinction lies in the nature of their operation. Server devices are designed for continuous operation and can handle substantial workloads. Conventional computers are typically used at home or in offices, averaging about 8 hours of daily use. They process a smaller volume of information. If a regular power supply fails, it’s unlikely to have serious consequences. However, a server cannot afford to fail because every minute of downtime impacts the company’s budget and reputation.
As a result, server power supplies are more reliable, and in case of a malfunction, they can be quickly replaced without disrupting the entire system.
What factors are important to buy a Server Power Supply:
- Power Rating: The power rating of the power supply is crucial. It determines whether your computer can handle server upgrades, the risk of overheating, and electricity consumption. Power ratings are typically categorized as follows:
Low: Less than 600 Watts
Medium: 600-800 Watts
High: 800-1100 Watts
Maximum: More than 1100 Watts
To determine the required wattage for your computer, you can use a calculator, such as Cooler Master or MSI. It’s advisable to choose a power supply that is at least 30% more powerful than what you need to prevent overheating and component wear.
- Connector Types: The most critical requirement is having connectors that match your server’s motherboard. Typically, this is a 24-pin connector. Before purchasing, calculate the type and quantity of connectors you’ll need for your current setup and any future upgrades. Each processor usually requires a 4-pin or 8-pin connector, while a 6+2-pin connector is needed for the graphics card. SATA connectors are used for storage devices, Molex for older devices, and possibly connectors for water cooling. For a powerful system, it’s advisable to have multiple CPU connectors and GPU connectors.
- Cable Length: Cable length is primarily an aesthetic concern. Short cables give your system a tidy appearance, but cables shorter than 65 cm may not reach the connectors. If the cables are non-removable, you’ll need to find a way to hide them. Partially modular power supplies allow you to detach certain cables, which can save space, keep your workspace tidy, and make dusting easier. Cables also come in different visual styles, such as colored or braided, and can be round or flat.
- Cooling System:The quality of the cooling system affects the power supply’s longevity and noise level. There are three main types:
-Active Cooling. The fan runs continuously, common in budget power supplies. Downsides include noise and dust buildup.
-Semi-Passive Cooling. The fan stops at low loads. This is the most common type.
-Passive Cooling. No fan is present, making the power supply completely silent. However, these are expensive and rare.
Noise and lifespan also depend on the type of bearing used in the fan, with hydrodynamic bearings being preferable.
- Form Factor: The form factor refers to the physical dimensions of the power supply. The most common types are:
-ATX: The most widespread form factor, with dimensions of 15×8.6×14 cm. Most standard cases are designed for ATX power supplies.
-TFX: Designed for entry-level servers, with dimensions of 15×8.6 cm (width and length vary).
-SFX: Compact and easy to install due to their elongated shape, with dimensions of 8.5×6.52×17.5 cm.
-Flex ATX: Extremely small at 12.5×5.15×10 cm.
Notice: While the working principles of these power supplies are similar, they have their own design features. Remember that the compatibility of these characteristics with your specific server system is crucial. Choosing the right power supply ensures the stability and longevity of your server.
Functions of server power supply:
The power supply is responsible for several parts of your system:
- Expandability: If the power supply’s wattage is insufficient, you won’t be able to add an extra graphics card or a high-end processor.
- Stability: Lower-quality power supplies can lead to system instability, causing issues that are challenging to diagnose.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern devices help reduce power consumption.
- Cooling: The power supply contains a fan that directs air into the case.
The power supply case shields other components from radiation.
What is the most reliable power supply:
A reliable power supply should have:
- PFC (Power Factor Correction)
- A warranty of at least three years
- A PCI connector line
- Short-circuit protection
- A certification of bronze or higher
- A T-shaped power connector
Current reviews from specialists with positive feedback are particularly important. Only through these can you ensure that the PSU operates without issues and doesn’t overheat.
Read more: What is Server CPU
Different types of power supply:
- Linear Power Supplies
A linear power supply is, in many ways, the classic choice. It operates by taking the input voltage, and then, through a combination of transformers, diodes, and filters, provides a steady, direct current (DC) output. The process, however, can lead to some energy loss in the form of heat.
-Pros: Low noise and minimal ripple. It’s also a simple design with fewer components.
-Cons: Less energy-efficient compared to switching power supplies (which we’ll discuss next). These are larger and heavier due to the transformer as well.
-Best Uses: Ideal for environments where a low level of electromagnetic interference is essential. Due to its simplicity and minimal noise output, it’s a favored choice in audio, communication, and certain sensitive medical equipment.

- Switching Power Supplies
Switching power supplies, or switched-mode power supplies (SMPS), are the modern counterparts to linear ones.
These work by rapidly switching on and off to regulate the output voltage. This method is far more efficient and allows for a compact design. However, they can produce more electrical noise compared to linear power supplies.
-Pros: Highly efficient, minimizing energy wastage. Compact size due to the absence of bulky transformers
-Cons: Greater electromagnetic interference. The more complex design means more failure points.
-Best Uses: Widely utilized in computers, televisions, and almost any application where size and efficiency outweigh concerns over electrical noise.
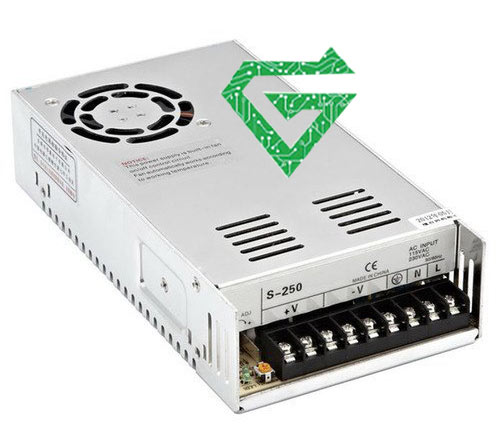

- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (U.P.S.)
This type of power supply is a lifeline in scenarios of power disruptions. As the name suggests, as the name suggests, it provides continuous power even if the main supply fails. It achieves this feat by storing energy in batteries and then switching to this stored power instantaneously during outages, ensuring no interruption.
-Pros: Immediate response to power interruptions. It can provide power long enough for systems to shut down safely or switch to an alternate power source
-Cons: Typically more expensive due to the inclusion of batteries. It requires regular power supply repair and maintenance, especially battery replacements
-Best Uses: Crucial for data centers, hospitals, and any operation where even a brief power outage could have serious consequences.
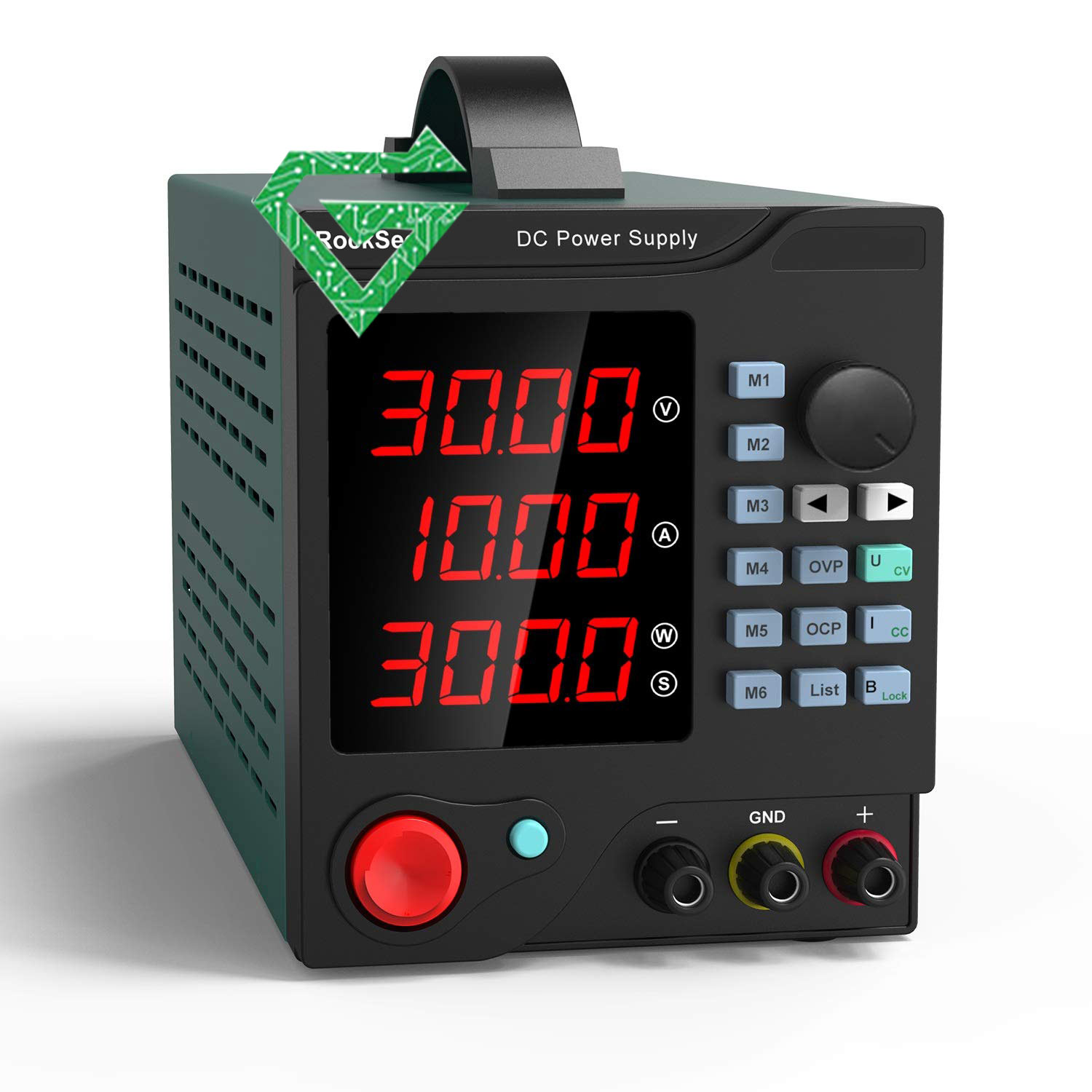
- Programmable Power Supplies
Programmable power supplies allow users to set specific voltage and current levels based on their needs. They can be controlled either manually through knobs and dials or digitally via software. This flexibility enables users to adjust power outputs for different tasks and applications.
-Pros: They’re versatile and can adapt to various needs and applications. Digital interfaces allow for precision and repeatability
-Cons: Typically more expensive due to their advanced features. They also may require training or familiarity with programming
-Best Uses: Laboratories, research, and development environments, and places where precise power control is essential.

- Modular Power Supplies
Modular power supplies are designed with separable components, allowing users to customize their setups. They can be tailored to fit specific needs, ensuring no excess capacity or deficiency.
-Pros: Scalable, allowing users to expand or modify without purchasing an entirely new unit. Enhanced maintenance due to component-wise replacement.
-Cons: Might have a steeper learning curve for configuration. Potential for higher upfront costs.
-Best Uses: Industries requiring scalability, such as manufacturing units or large-scale operations.

- High Voltage Power Supplies
As the name suggests, high voltage power supplies deliver higher voltages than standard units. They’re specifically designed to ensure safety and performance when working with high voltage applications.
-Pros: Ensures safe and stable high voltage outputs. Designed with specialized safety features.
-Cons: More expensive due to specialized components. Requires careful handling and proper safety measures.
-Best Uses: Automatic industrial equipment, charging energy storage systems, centralized bus power, particle accelerators, or high-powered lasers.

- DC-DC Converters
A DC to DC converter converts direct current (DC) voltages from one level to another, making them crucial in various applications where precise voltage adaptation is needed. They can step up or down depending on the use-case and configuration.
-Pros: Efficient energy conversion with minimal wastage. The compact design suitable for a range of applications.
-Cons: Potential for electrical noise in some models. Efficiency may decrease at very low or high input voltages.
-Best Uses: Battery-operated devices, renewable energy systems like solar panels, and devices that need multiple voltage levels.

- AC-DC Power Supplies
An AC to DC converter transforms the high voltage alternating current (AC) that powers our homes and businesses into a usable, steady direct current (DC) that the majority of electronic devices require. This ensures that devices receive the correct voltage and current levels to operate efficiently and safely.
-Pros: Safeguards electronics from the inherent fluctuations in AC mains. Universal necessity makes it a widely researched and optimized product. Eliminates the need for devices to handle complex voltage transformations internally.
-Cons: Physical conversion processes can introduce inefficiencies and heat. Design and quality disparities across brands can lead to varying levels of performance and safety.
-Best Uses: Desktop computers, home entertainment systems, office equipment, and virtually any electronic device plugged into a wall socket.

- External (or Wall-mount) Power Supplies
External power supplies represent a design decision to keep the power transformation process outside the main device. By doing so, devices can stay cooler, become more compact, and avoid internal complexities linked to power conversion.
-Pros: Mitigates the risk of heat-related issues inside the primary device. Also makes device certifications easier, as external power supplies can be standardized. A single device can be used globally, with different power supplies catering to regional voltage standards.
-Cons: Physical bulk can crowd power strips and outlets. Loss or damage requires a specific replacement, sometimes ata significant cost.
-Best Uses: Laptops, modems, small kitchen appliances, and specialty lighting setups.

- Battery Chargers
Battery chargers are devices used to inject energy into secondary cells or rechargeable batteries. They do this by driving an electric current through them. They’re becoming more and more prevalent with the rise of autonomous robots in the workplace.
-Pros: Ensures optimal battery health and longevity. These also offer flexibility as many chargers can recharge various battery types. They’re even equipped with features that prevent overcharging.
-Cons: Using an incompatible charger can damage batteries. Plus, some chargers can be slow, especially when charging large batteries.
-Best Uses: Charging batteries for tools, equipment, mobile devices, electric vehicles, robots, and more.
Read more: What is HP Server Hard Drive
- Redundant Power Supplies
Redundant power supplies (RPS) are systems designed to provide continuous power, even if one or more power sources fail. They offer peace of mind knowing your operation will remain running no matter what happens. They’re a must-have in mission-critical scenarios where power failure is not an option – be it the medical field or in industrial workplaces.
-Pros: Ensures high uptime with an immediate switch-over to backup. This ensures seamless operations. Also protects against data loss and service disruptions.
-Cons: Can be more expensive due to the need for multiple power supply units. Requires more space for installation.
-Best Uses: Data centers, hospitals, emergency services, industrial processes, and other critical systems where power interruption is not an option.

- DIN Rail Power Supplies
A DIN rail power supply is a compact, standardized device designed for mounting on DIN rails. It is commonly used in equipment rack installations and industrial control systems.
-Pros: Streamlined installation and removal process. Saves space in enclosures and offers better heat dissipation due to its mounting style.
-Cons: Might not be suitable for heavy-duty power requirements. Physical size limitations can affect power capacity.
-Best Uses: Industrial control systems, automation systems, and environments requiring modular setups with easy maintenance and swap-out capability.

- Inverters
Inverters play a crucial role in converting direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC) which is typically used by most household and industrial devices.
-Pros: Enables the use of standard AC-powered devices in DC environments while ensuring efficient energy conversion. Often has features to regulate output and protect against surges.
-Cons: Energy losses during conversion can be costly. These also require compatibility checks to ensure proper voltage and frequency outputs.
-Best Uses: Solar power setups, backup power systems, and mobile or remote locations where only DC power is available but AC devices need to be powered.

- Rack Mount Power Supplies
Rack mount power supplies are designed for easy integration into standardized 19-inch equipment racks. They provide a convenient and organized solution for multiple power supply requirements.
-Pros: Consolidated power management in one rack. Often equipped with advanced monitoring and control features. Scalable and typically modular in design.
-Cons: Can get expensive for high-capacity needs. Needs proper ventilation and heat management in the rack setup.
-Best Uses: Data centers, server rooms, audio/video setups, and other professional environments requiring organized power distribution and management.

- Custom Power Supplies
Last but certainly not least in our list of power supply types is the customized power supply. These are the solutions for unique applications or specific requirements that aren’t met by off-the-shelf products. They’re designed to precise power supply specifications to ensure they fit perfectly into a system’s needs.
The key is to find a partner you can trust in bringing your custom power supply to life – and we fit the bill here at Bravo Electro. More on that later.
-Pros: Tailored to exact requirements, ensuring optimal performance. You can integrate features not found in standard models to go above and beyond the norm.
-Cons: Longer lead times due to the design and production process. Can be more expensive than standard units. Finding the right design can be challenging, too. All this is alleviated with the help of Bravo Electro, though!
-Best Uses: Specialized industrial equipment, research facilities, or any scenario where specific voltage, current, or form factor needs can’t be met by standard power supplies.
Read more: What is HP server
What are advantages and disadvantages of AC power supplies:
The advantages of alternating current (AC) power sources are that they are a widely used form of energy, are suitable for the transmission and distribution of electrical energy, use the standard AC voltage of electrical networks, and have low energy loss. However, the disadvantages of AC power supplies are that sometimes high voltages can be dangerous, some electronic devices may require direct current (DC), high-frequency switching can produce electromagnetic noise, and high-voltage AC power supplies can be poor in terms of energy efficiency. Therefore, depending on the application requirements, the advantages and disadvantages of AC power supplies must be taken into account and designed appropriately.
What are advantages and disadvantages of DC power supplies:
The advantages of direct current (DC) power supplies are that they provide a suitable energy source, especially for electronic devices, provide stable output and high energy efficiency. DC power supplies make it easy to supply electronic circuits with the desired voltage and current, which ensures the proper operation of sensitive devices.
However, the disadvantages of DC power sources include factors such as the difficulty in transporting energy over longer distances than AC and the need to convert to AC in some applications. Therefore, the advantages and disadvantages of DC power supplies must be considered depending on the needs of the application.
Conclusion:
A reliable power supply is essential for any server, ensuring stable performance and protecting critical components. Using high-quality server accessories, such as Ram server, CPU Server, Motherboard Server, and Hard server, further enhances your server’s efficiency, longevity, and overall reliability. We are in Atech.ae for providing the best of them in high quality.





