What is HP server

server is a sample of a computer program or device that accepts and responds to requests made by another program, known as a client. Imagine you need to eat some food, you will need to go the fridge to get it, so the fridge will be your server to store all the food (files) inside, while you are the client that want to get food (information) to consume.
So a server gets information to computers that connect it. Users can connect to servers by local network or wide network as the Internet, after that, they can access to programs and files from server. Therefor servers are important. in this article, we want to survey HP server, Different types of servers and also different generation in HP servers. Follow us to end.
What is HP server:
A server is a computer or device on a network that manages network resources. It has the ability to store files and applications, provide you access to those files and applications, and processes requests from multiple users or devices at once. Servers are responsible for handling the requests of connected clients by providing them with the data they need or the application they want to use.
ProLiant is a brand of server computers that was originally developed and marketed by Compaq, Hewlett-Packard (HPE), and currently marketed by Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE). ProLiant servers were first introduced by Compaq in 1993, succeeding their SystemPro line of servers in the high-end space.
After Compaq merged with HP in 2002, HP retired its NetServer brand in favor of the ProLiant brand. HP ProLiant systems led the x86 server market in terms of units and revenue during first quarter of 2010. HPE now owns the ProLiant brand after HP split up into two separate companies in 2015.
HP company has different types of network equipment such as computer, laptop, RAM Server, Motherboard Server and etc. also It has some server equipment like HP Hard server, and HP server Memory that are sold in network equipment market.
What does a server do:
A server stores, sends, and receives data. Mainly, it “serves” something else and exists to provide services. A computer, software program, or even a storage device may act as a server, and it may provide one service or several. Totally, a server is a computer or system that provides resources, data, services, or programs to other computers, known as clients, over a network.
In theory, whenever computers share resources with client, machine they are considered servers. also a server is responsible for managing and distributing resources across a network. This includes handling data storage and sharing, allowing you to access shared documents and applications, hosting websites and webpages, sending emails, setting up file sharing, providing secure access over the internet through VPNs, as well as providing additional services depending on what kind of server it is.
At its core, a server works by managing and distributing resources across connected clients. When a client sends a request for something to the server, it processes that request first by looking up what resource it needs from its local storage, such as pulling up an application or document stored in its databases. Once it recovers that information, it sends it back to the client machine for them to complete their task.
Comparing different generation in HP servers:
HP Enterprises began producing the ProLiant Server Gen 8 in 2012. Two years later, Gen 9 was released. In late 2017, the Gen 10 became available. With 5 years of technological advancements between the Gen 8 and Gen 10, there are distinct differences between them, but which server generation is right for your business?
We’ll compare the HPE Server Gen 8, Gen 9 and Gen 10 Servers to highlight the features that were added and how expandability increased with each new generation.
-
HPE ProLiant Gen10:
The HPE ProLiant Gen10 server portfolio claims to be the server to meet your diverse workload needs. Indeed, it is an improvement on the Gen9, offering a 71% performance increase and a 27% increase in core, thanks to the latest processors from Intel. Additionally, it has security enhancements, the HPE Secure Compute Lifecycle, to protect your server. These include firmware protection, malware detection, and firmware recovery.
The new Intelligent System Tuning allows you to increase or decrease performance based on the specific workload to save energy and enable higher performance across processors. The Gen10 servers have also been designed with the hybrid cloud in mind. The new scalable processors from Intel are workload-optimized for hybrid cloud infrastructures or demanding enterprise data centers. some improvements of HPE ProLiant Gen10 such as HPE ProLiant DL380 Gen10 Server, include:
- 66% more memory bandwidth to increase performance for memory-intensive applications.
- 27 times faster checkpoint operations to enable faster business operations
- 14% more processor cores
- 33% greater memory capacity

-
HPE ProLiant Gen9:
The Gen9 server portfolio delivers the right compute for any business size, workload size or any environment. The Gen9 servers provide three times the computing power per watt than the previous generation. Over the life of the server, this can be a cost savings of 62%. The Gen9 also has an improved workload performance for business-critical applications up to 4 times! This increased performance is thanks to innovations in storage, memory, and networking.
Additional improvements include:
- Triple the compute capacity of the Gen 8 and increased efficiency across multiple workloads.
- 66 times faster service delivery, made possible with automation to save admin time and reduce errors
- Upgrade to DDR4 memory from DDR3. Reaches memory speeds of up to 2,133 MHz per second.
Read more: What is HP Server Hard Drive
The HPE ProLiant Gen9 servers such as HP ProLiant DL380 Gen9 Server were also built for expandability. They offer more options than the Gen8 or Gen10, with 26 CPU Server selections, 50% more L3 cache than Gen8 and up to 18 additional cores. There is easy access for processor installation. Enterprise-grade RAID controllers improve data availability, performance, and storage capacity. Gen9 also has SmartDrives, SmartMemory (also a Gen8 feature) and flexible network adapters for easy option configuration and increased efficiency.

-
HPE ProLiant Gen8:
The HPE ProLiant Gen8 includes many new improvements compared to previous generations. With this generation, the small and large form factor hot swap plug drive carriers were completely redesigned to be more intuitive. Thermal Discovery Services have been added that reduce energy usage by 10% and increase compute capacity. Additionally, with Gen8, Smart-Memory supports DDR3-1600, bringing the memory to 1600MHz. This is a new feature with the Gen8 and increases memory by 20% over previous generations. Also new with Gen8 servers are the IO Accelerators, which increase application performance. The IO Accelerators use existing internal server slots for a zero-footprint server integration.

-
HPE ProLiant Gen11:
HPE Gen11 servers offer several improvements over HPE Gen10 servers, making them a better choice for organizations. Here is a summary of why HPE Gen11 is better than HPE Gen10:
- Enhanced Performance: HPE Gen11 servers deliver optimized performance for a wide range of workloads, including AI, analytics, cloud-native applications, machine learning, Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), and virtualization. Compared to the previous generation, Gen11 servers support twice as much I/O bandwidth, 50% more cores per CPU, and 33% more high-performance GPU density per server. These improvements enable organizations to handle more demanding applications and achieve higher performance levels.
- Intuitive Cloud Operating Experience: HPE Gen11 servers come with HPE GreenLake for Compute Ops Management, which provides an intuitive, automated cloud operating experience. This subscription-based service simplifies server management by offering a cloud-native management console. It allows customers to securely automate the process of accessing, monitoring, and managing servers, regardless of the compute environment’s location. The console provides simple, unified, and automated capabilities, giving customers global visibility and insight into their compute resources.
- Trusted Security by Design: HPE Gen11 servers continue to prioritize security. They feature the HPE Silicon Root of Trust, an industry-exclusive security capability that protects firmware code from malware and ransomware. The servers also include new security features such as device component verification and authentication, platform certificates, Secure Device Identity (iDevID), and Trusted Platform Module (TPM) monitoring. Additionally, HPE’s Trusted Supply Chain ensures end-to-end security by offering certified servers with hardened data protection during the manufacturing process.
- Flexibility in Processor Options: HPE Gen11 servers support a diverse set of architectures, including 4th Generation AMD EPYC™ processors, 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors, and Ampere® Altra® and Ampere® Altra® Max Cloud Native Processors. This flexibility allows organizations to choose the processor that best suits their specific workload requirements.
- Extended Support and Availability: HPE has extended the support for Gen11 servers from three to up to seven years, providing organizations with longer-term support and peace of mind. The servers are available to order worldwide, with HPE GreenLake offering a pay-as-you-go consumption model for organizations looking to transition to the next generation of compute.

Choosing the Right Generation for Your Needs:
The consistent advances of the HPE ProLiant server portfolio generations show great technological improvement across the last three generations, but that doesn’t mean that the older generations are obsolete! When it comes to choosing the server that is right for your organization (and budget), there are a lot of configurations and options to consider from the Gen8 and Gen9 server portfolios.
If you are already running Gen8 servers and are looking to supplement for greater storage or processing, adding another Gen8 server will be significantly less expensive than a full upgrade.
Or, perhaps, you’re looking for a server that’s configurable and easily expandable, as well as cost effective. The Gen9 is powerful and highly customizable and expandable, making it a logical and budget-friendly choice. Eventually, the HP server GEN11 is the best of all. You have all features and benefit in it.
Read more: What is Server CPU
Different series of HP server and comparing them:
HP servers are separated into four main product lines; ML, DL, BL, SY, and XL (Apollo). which generally denote form factor.
The ProLiant ML line comprises tower-based servers (convertible to rack mount) with capacity for internal expansion of disks and interconnects, while the DL line comprises general purpose rack mount servers. The BL line comprises blade servers which fit within the HP Blade System, the SY comprises the Synergy Blades, and the XL (also known as Apollo) line comprises servers for scale out and High-Performance Computing environments. The Micro Server product line addresses small and home businesses.
ProLiant servers are also split into several series which denote processor configuration. The 100, 200, 300 and 400 series comprise single and dual socket capable systems, the 500 and 600 series comprise quad socket capable systems, and the 700 and 900 series comprise eight socket capable systems. The 900 series supports up to 80 CPU cores and up to 4 TB of RAM.
- ML (Modular Line): ML server is tower-based. It aims towards maximum expandability. ProLiant ML models are Tower systems produced for remote and branch offices as well as growing businesses. Developed for expandability and adaptability the ProLiant ML range is perfect for developing businesses where their requirements may grow. Favoured for their naturally quieter operating, due to larger fans, ProLiant Tower servers are often featured in offices and home-labs where they rarely produce more noise than a standard workstation. Part of the HP Tower server range is the HPE Micro Server. These systems are ultra-compact low-cost systems designed for small or home offices and enthusiasts. Offering the user friendly platform ClearOS (optional) HP Micro Servers use an intuitive GUI for your ease of use. Favored for on-site backups and small RAID arrays MicroServers can provide a simple solution for onsite backup needs.
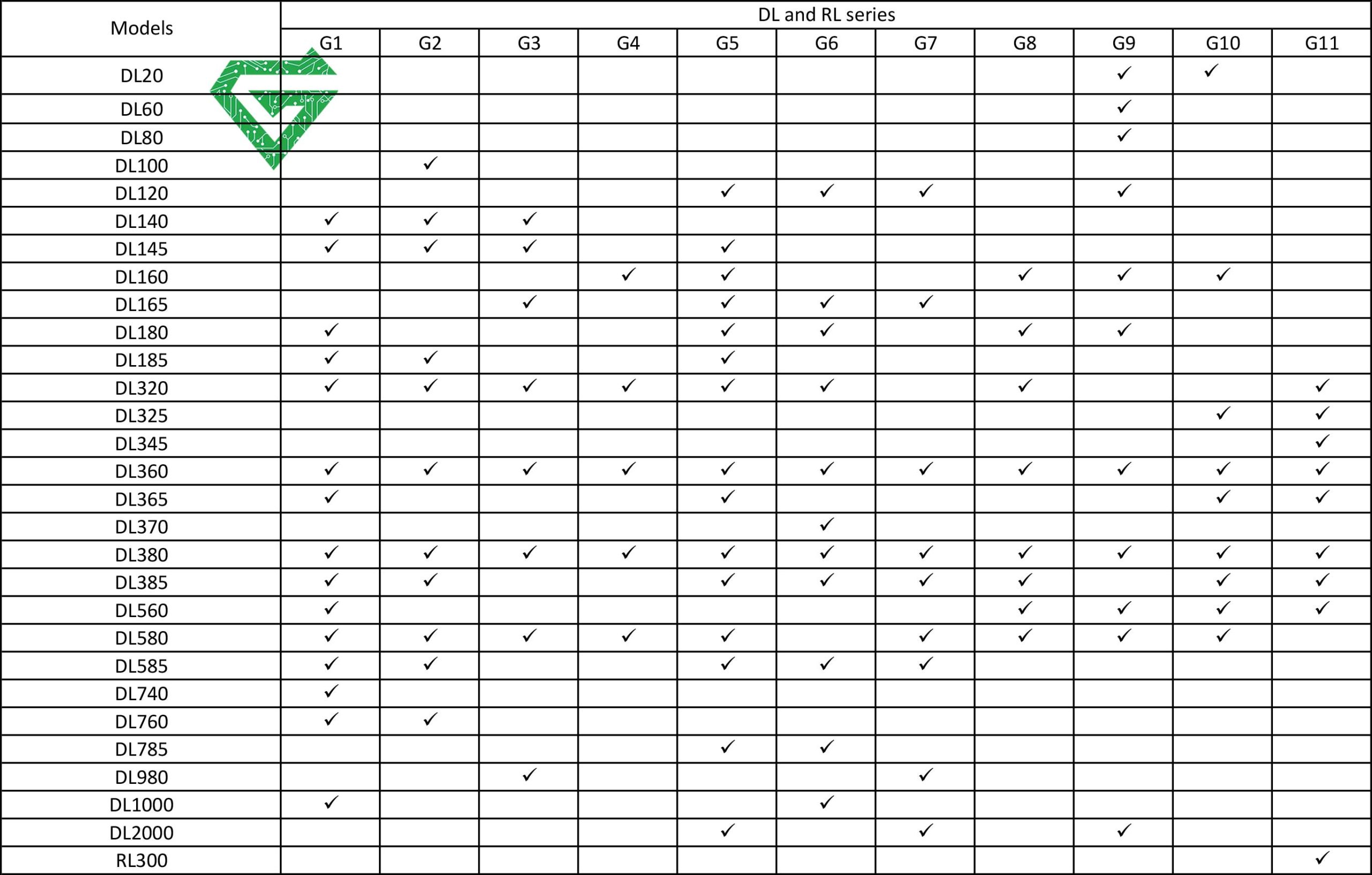
- DL (Density Line): DL server is rack-based. It goals towards a balance between density and computing power. The ProLiant DL models are rack-based systems with an aim to be produce the perfect balance of performance, management and energy efficiency. As a general rule the higher the model number in the ProLiant range the higher powered the system is for example, server models from the DL range start with affordable, dense units such as the DL20 or DL120 and range up to the DL580 series made for very intense workloads.
- SL (Scalable Line): SL server is rack-based. It is mostly used in data centers and environments where a maximum of computing power is desired. Ideal for hyper-scale and HPCs the ProLiant SL range prioritises power per ‘u’ through increased density and shared chassis housing. Through the use of HP Scalable Line systems lower operational costs, increased deployment speed and greater energy efficiency can be achieved. Purpose built for data centers, systems such as the SL6500 offer true flexibility through a flexible 8 half-width node 4U system. As demand for hyperscale, hyper-converged and high-performance computing systems increased HPE developed the Apollo series to better fit the needs of these demanding environments. Made to be incredibly scalable, cost effective and powerful the Apollo range perfectly suits demanding applications in professional enterprises.
- BL (Blade Line): BL server is enclosure-based. It is made specially for use in a blade enclosure and cannot be used without such. Blade systems aim towards maximum density and manageability at limited rack space. HP ProLiant BL range offers a fully converged infrastructure for medium and enterprise data centers. BL systems are combined together in a HPE c3000 or c7000 shared chassis providing a truly redundant, energy efficient and cost effective solution for large enterprises and data-centers alike. Featuring 16 half-width, or 8 full-height, blade bays the HP c7000 is favored for its flexibility allowing for 8 interconnect modules, 2 Onboard Administrator modules, 10 Hot-Swap Redundant fans (model dependent) and 6 single or three phase high efficiency power supplies. The Blade-System enclosure provides back and forth compatibility accepting both new or old blades allowing for gradual expansion in budget constrained environments.
Why would I use a server?
Servers offer you many advantages over individual workstations for tasks such as data storage and sharing, document collaboration among multiple users, hosting websites or webpages, setting up secure connections over the internet via VPNs etc. It can be more beneficial for you to having access to centralized resources provided by a powerful computer than just relying on individual workstations with limited capacity and capabilities.
What are some benefits of using a server?
The uses for servers are wide-ranging but most benefit from faster speeds when compared with local devices due to their higher processing power. They can also be more efficiently managed than separate machines since all resources can be centrally administered rather than individually installed/configured on each machine.
Furthermore, they can offer greater levels of security since only authorized people have access to them thereby preventing hackers from accessing sensitive information stored on them directly without proper authentication credentials first being supplied by users attempting to enter them remotely.
Lastly, they allow organizations to scale easily making them an even more cost efficient alternative when dealing with large number of users needing access simultaneously within one company’s network infrastructure.
Read more: What is a server power supply
Different types of servers:
There are many different types of servers used in networks today. Common examples include mail servers which handle email delivery; web servers which host websites; game servers which host online video games; application servers which run custom software; file servers which store, manage and share files between computers; print servers which manage printing jobs from multiple devices; database servers which store information in databases; as well as proxy, media streaming, cloud storage and virtualization servers.
There are different types of servers; WEB SERVER, EMAIL SERVER, PRINT SERVER, GAME SERVER, PROXY SERVER and STREAMING VIDEO SERVER.
- WEB SERVER: If you’re online and looking at a webpage, you are accessing a server. Viewing the web through your browser requires getting data from a web server for the text, images, videos, and any other components you can view on a webpage. When you send or receive files through the internet, download apps or programs, or even save your work files to the cloud, you are interacting with a variety of internet servers.
- EMAIL SERVER: If you use a web-based program, such as Gmail or Yahoo!, to access your email account, you probably rely on a web server to handle your messaging. For those consumers who prefer to use a computer-based program, such as Outlook, you access a specific email server that supports the sending and receiving processes. If you see references to IMAP, POP, or SMTP when using email, you are connecting to a third-party email server.
- PRINT SERVER: Do you send print jobs to your computer over WiFi? The management of print files and printer tasks is done through a print server.
- GAME SERVER: Gamers know all about these. Loading an online game requires you to connect to a server. Each game generally has its own server. If you’ve ever waited a long time for a game to load, congestion on the server may be the issue. From the biggest online computer games to the smallest, app-based smartphone games, they all use servers to send and receive the information necessary for gamers to play.
- PROXY SERVER: Any time there is a third-party intermediary between a person’s computer and another server, this middle-man is known as a proxy server. Proxies have useful roles in filtering content, speeding up internet traffic, and keeping unauthorized users from accessing the network. Most business internet connections use proxy servers on their networked computers to keep data safe and to ensure their workers only use permitted web functions.
- STREAMING VIDEO SERVER: When you open some tv platforms such as Netflix on your phone or movies from site on your smart TV, you are using a video server. All of those movies and TV shows are saved as data on these servers and are pushed out to you when you request them.
In addition to those explained above, there are many, many other server types including fax servers, file servers, database servers, chat servers, audio servers, and application servers. Anytime data is stored and sent, a server is involved. There are some examples for every categories that explained above, during this article demonstrate them more!
Read more: Upgrading Your Server with the Best CPU RAM and GPU
How do I connect to a server:
Connecting to a server usually requires entering an IP address (Internet Protocol) into your computer’s web browser or FTP (File Transfer Protocol) client program. Depending on your type of server connection, you may also need other credentials like usernames/passwords or keys when connecting to that server. Once connected successfully, you can access any of its shared resources such as documents folders or applications running on that server.
What kind of software is required to run a server?
In general, most servers require an operating system like Linux or Windows. Depending on the type of server you’re running, you may also need additional software such as web servers (like Apache or IIS), database servers (like MySQL or Oracle), mail servers (like Sendmail), application servers (like Java or .NET) and media streaming servers.
What are the different components of a server:
The most common server accessories include a CPU Server (central processing unit) which is responsible for actual data processing, Ram server (random access memory) which handles short-term storage, disk drives which store data persistently and provide additional storage space, NICs (network interface cards) which allow the server to send and receive data across networks; power supplies which supply power to all other components within the server and cases or racks, which house all the above-mentioned components.
Servers exist for everyone:
If you thought a server was something only tech pros encounter, you now know they play a role in everything we do online. The world wide web wouldn’t exist without servers, and these innovative and adaptable tools keep our home and business networks safe and operational.
How much secure is my data stored on a server?
Servers typically offer greater levels of security than could be achieved with individual machines due to increased control over who can access what resources. This is because everything stored on the server is centralized allowing administrators to assign permissions as well as revoke them when needed easily thereby preventing hackers from accessing sensitive information stored directly on them without proper authentication credentials being supplied by users attempting remote entry into them first.
Furthermore, they offer other security measures such as encrypted connections between users and servers as well additional measures like implementing firewalls against potential intruders.
Why do some companies prefer cloud-based services instead of physical servers?
One of the main reasons why many companies are opting for cloud-based solutions over physical ones is due to cost efficiency and scalability. Cloud computing allows companies to access powerful resources with very little upfront costs since they pay for what they use only and can scale easily whenever necessary.
Plus, there’s no need to maintain the hardware which eliminates extra costs associated with traditional server setups such as maintenance fees, electricity bills, etc. Furthermore cloud-based services offer better performance than actual machines since all data is stored remotely rather than locally.





