What is OSI Model
For communicating systems over a network uses OSI Model that has different layers. Every layer has special operation, ranging to high-level application interface.
The OSI Model is a base definition that every network manager must know it. In this article, we will explain to you and all aspects of this Model. we are here to write useful articles about network equipment and the protocols that supported by them, so follow our articles in Atech blogs.
What is OSI Model?
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection Model) model is a conceptual model used to describe the functions of a network system. It defines a hierarchical architecture that logically divides the functions needed to support system-to-system communication.
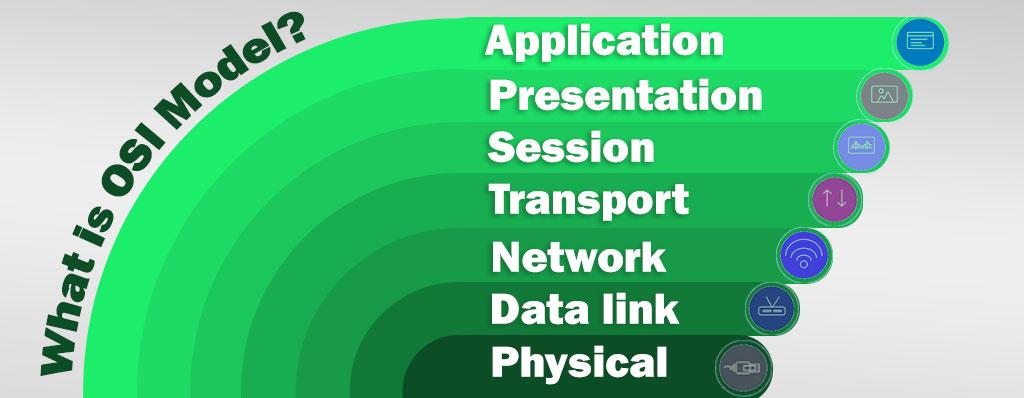
There are seven layers in total that perform specific tasks and functions. It is a reference model that shows how different applications talk to each other on the network and plays an important role in passing messages between systems.
The OSI Model is common language for networking and makes a common ground to communicate variety systems. In simple language, we can say, OSI Model provides a standard for different computer systems to be able to communicate with each other.
Every layer in OSI Model does specific task and be able to connect with layers above and below. That introduce each layer and their operation in continue.
Layers of OSI Model:
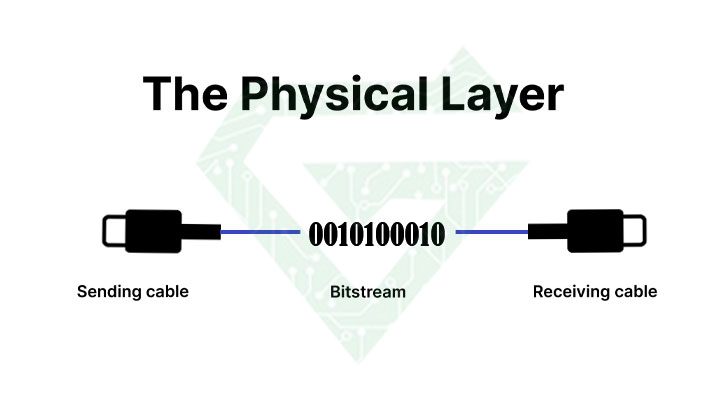
- Physical layer: Transmits raw bit stream over the physical medium. The first layer of the OSI reference model is the physical layer. This layer is responsible for the actual physical connection between devices such as network switch and cables. The physical layer contains information in the form of bits. It is responsible for transmitting bits from one node to another. When receiving data, this layer converts the received signal into 0s and 1s and sends them to the Data Link layer, which reassembles the frame.
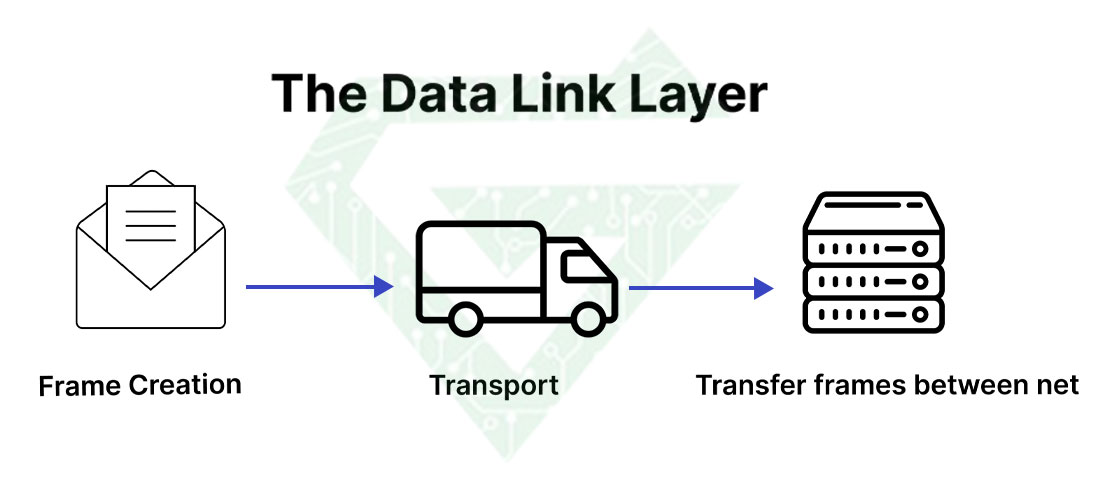
- Data link layer: defines the format of data on the network. this layer is similar to network layer. There is difference between them, that this layer makes transmit between two devices easily. Data link layer got packets from network layer and then break them in smaller pieces (frame). This layer likes network layer is responsible for flow control and error control in intra-network communication. The Data Link layer is responsible for sending messages from node to node. The main task of this layer is to ensure that the data transfer from one node to another in the physical layer is error-free. When a packet enters the network, it is the job of the DLL to forward it to the host using its MAC address.
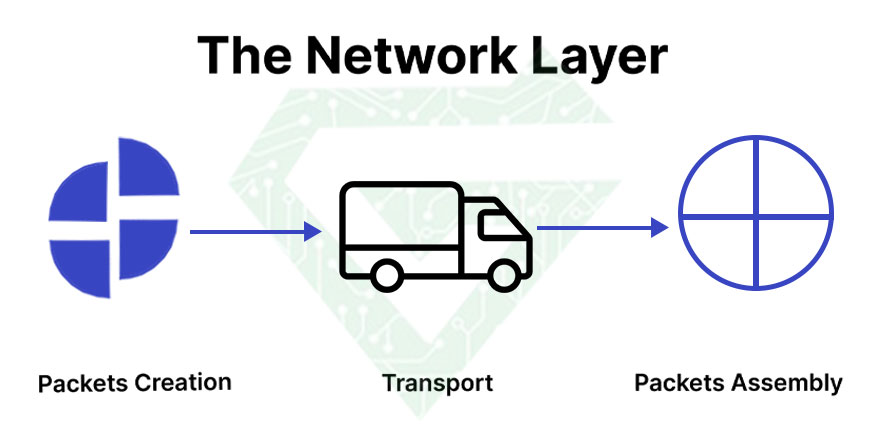
- Network layer: decides which physical path the data will take. The network layer makes transferring easily. If the two devices communicating are on the same network, then the network layer is unnecessary. The network layer in the OSI model is a routing layer that coordinates the parts of a data conversation to ensure the transfer of files. While the second layer handles how the physical layer data is transferred, this layer organizes this data for transmission and assembly purposes. It manages all routing protocols and finds the best way to transfer data from one network to another. The network layer is also responsible for logical addressing, for example IPv4 and IPv6. Routers make forwarding decisions based on IP address information and perform routing. The network layer finds the destination using logical addresses such as IP (Internet Protocol). The IP addresses of the sender and receiver are placed in the header based on the network layer. In this layer, routers are an important component that is used to completely route the data to where it is needed between networks.
Read more: DDoS Attack and all about it
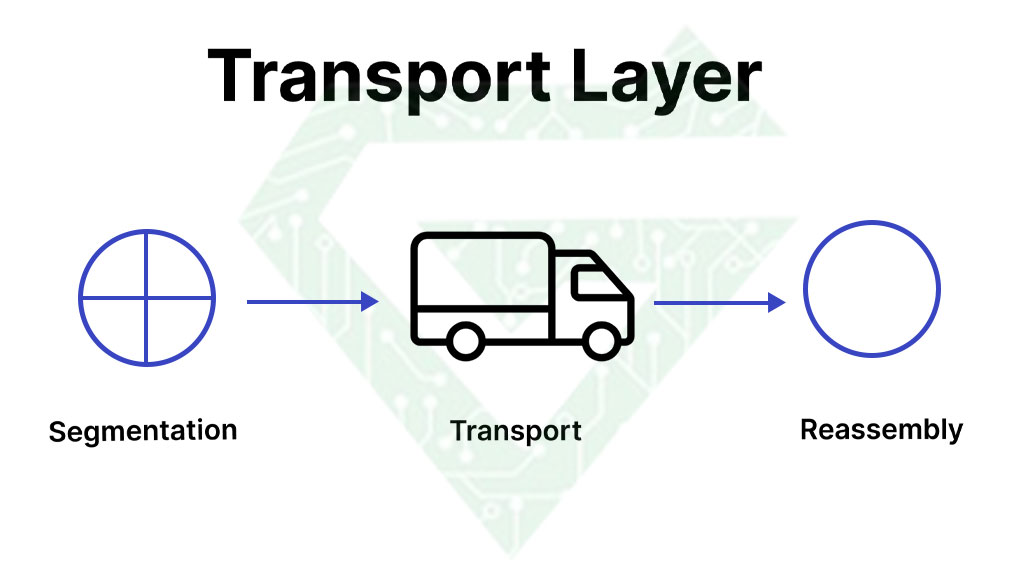
- Transport layer: transmits data using transmission protocols including TCP and UDP. The transport layer communicates between two devices. This layer got data from session layer and breaking it up into chunks before sending to layer 3. This layer on receiving device is responsible for reassembling the segments into data the session layer can consume. In this layer, common encryption and firewall security methods occur. The transport layer in the OSI model focuses on two protocols: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Data Protocol). Industry experts consider TCP to be a reliable or connection-oriented protocol.
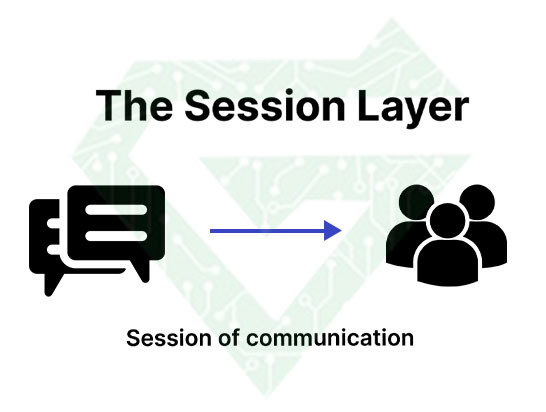
- Session layer: maintains connections and is responsible for controlling ports and sessions. This layer uses for opening and closing communication between two devices. The session layer stays open till all data transfer and close immediately. This process avoids wasting resources. This layer matches data transfer with checkpoint either.
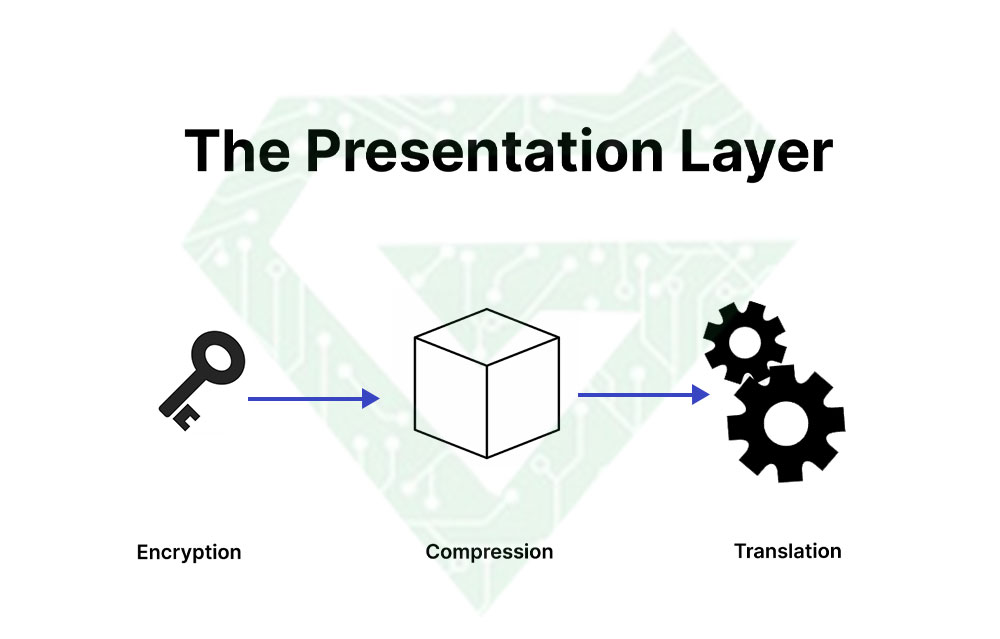
- Presentation layer: ensures that data is in a usable format and is where data encryption occurs. The sixth layer used for data presentable for applications to consume. This layer is responsible for translation, encryption and compression of data. Finally, the Presentation layer is also responsible for compressing the data it receives from the application layer before handing it over to Layer 5. This reduces the number of bits that need to be transmitted over the network.
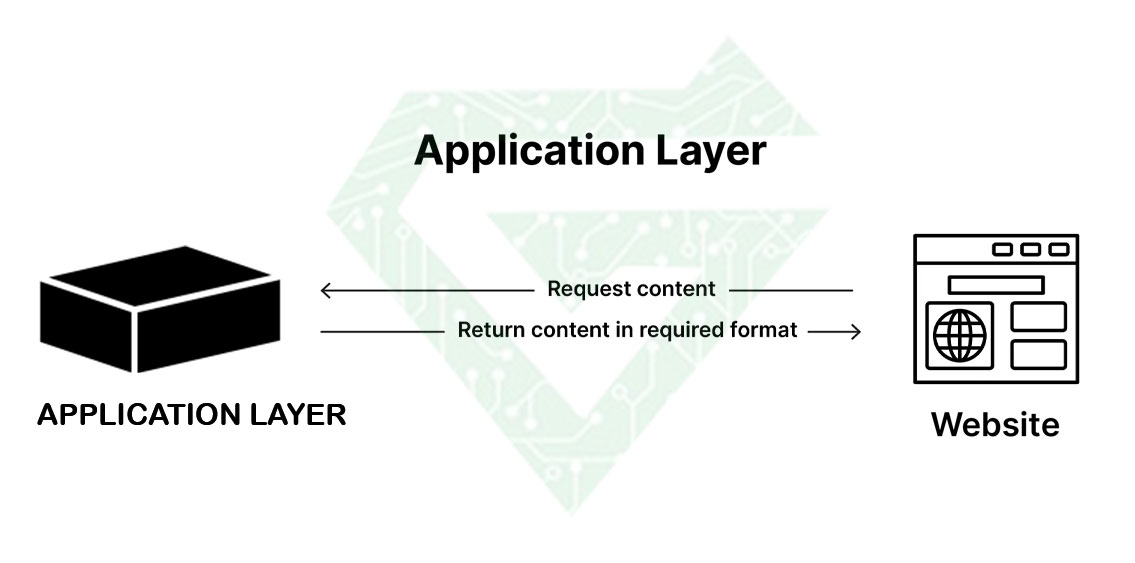
- Application layer: human-computer interaction layer, where applications can access the network services. In this layer interact data and user together. Software application such as email client, web browser uses this layer. Another protocols, for instance SMTP and HTTP include this layer.
What are the tasks of Data link layer?
- Framing: Framing provides a way for the sender to convey a set of important bits to the receiver. This can be done by attaching special bit patterns to the beginning and end of the frame.
- Physical Addressing: After the frame is created, the Data Link layer adds the physical addresses (MAC addresses) of the sender and/or receiver in the header of each frame.
- Error Control: Provides 2 error control mechanisms where it detects and retransmits damaged or lost frames.
- Flow Control: The data rate must be constant in both directions or the data may be corrupted, so flow control coordinates the amount of data that can be sent before an acknowledgement is received.
- Access Control: When a single communication channel is shared by multiple devices, the MAC sublayer of Layer 2 helps determine which device has control of the channel at a given time.
Read more: What is Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
What are the tasks of Physical layer?
- Bit synchronization: The physical layer provides bit synchronization by providing a clock. This clock controls both the transmitter and the receiver and thus provides synchronization at the bit level.
- Bit rate control: The physical layer also determines the transmission rate, i.e. the number of bits transmitted per second.
- Physical topology: The physical layer determines how different devices/nodes are arranged in a network, such as a bus, star or mesh topology. (You can click the link to learn more about mesh wireless networks.)
- Transmission mode: The physical layer also determines how data flows between two connected devices. Different transmission modes are possible: simplex, half-duplex and full-duplex.
Why is OSI Model important?
Although the internet doesn’t follow OSI Model, this model is useful for troubleshooting network. there is no difference between a laptop that is only for one person or a website that works for a lot of people, when you can’t connect the internet to your device will made a lot of problems. OSI Model helps to break sown the problem and solve them that is really valuable.
How to communicate in OSI Model?
The OSI Model designed as an application, that can connect in a network with another application on different devices. Without complexity of application and underlying systems.
For doing this task, using different standards and protocols to communicate with layer above and below. By chaining all layers and protocols, complex data communications can be sent from one high-level application to another.
- The sender’s application layer transmits data communication down to the next lower layer.
- Each layer adds headers and addressing to the data before passing it on.
- Data communication moves down the layers until it is eventually transmitted through the physical medium.
- At the other end of the medium, each layer processes the data according to the relevant headers at that level.
- At the receiver end, data moves up the layer and is gradually unpacked until the application at the other end receives it.
Advantages of OSI Model:
This model can divide network communication into 7 layers that make understanding and troubleshooting easier.
The OSI Model make network communication standard because each layer has fixed protocols and operations.
The OSI Model diagnoses network problems is easier.
Every layer can have update separately and it helps to improve easier.
Disadvantages of OSI Model:
Having 7 layers in OSI Model maybe is complicated and difficult for beginners.
In real network, most of the systems used TCP/IP protocol, so you can’t perform OSI always.
Each layer in OSI Model has collection of policy and rules that can make the processes less efficient.
This model is a theoretical framework that is great for understanding concept but not always practical for implementation.
Conclusion:
With OSI Model we can understand the movement of data better. This model has 7 layers that we have introduced all of them in this article. OSI Model is a conceptual model, but it uses for troubleshooting and understand network issues.
The network manager and engineers can use this model to organize and model networked system architectures. This model has ability to decompose a system into smaller, manageable parts that made it easier for people.





