Different types of Cisco Fiber Optic Module

Network Module is one the network equipment that designed by different companies and in these modules are essential components in network switches, routers and other network devices o enable high-speed optical communication and having better operation.
One the company which is really famous in producing network equipment. Cisco offers a variety of fiber optic modules that support different network speeds, distances and form factors.
Different types of Cisco Fiber Optic Module:
Cisco fiber optic modules come in several types based on the form factor, data rate, and supported distance. Common types include SFP, SFP+, QSFP, QSFP+, and newer standards like QSFP28 and QSFP-DD.
Each module type is designed to support specific applications, from short-range data center connections to long-haul backbone links. The choice of module depends on your required speed (1G, 10G, 40G, 100G, or higher), fiber type (single-mode or multi-mode), and distance.
-
SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable): Supports 1 Gbps speeds. Used for both multi-mode (e.g., SX) and single-mode (e.g., LX) fiber. Common in enterprise access layers.
-
SFP+: An enhanced version of SFP that supports 10 Gbps. Used in data centers and distribution layers.
-
QSFP (Quad Small Form-Factor Pluggable): Supports 40 Gbps connections. Often used for high-speed aggregation or data center spine-leaf architectures.
-
QSFP+: A more advanced version of QSFP, also used for 40 Gbps, with better performance and sometimes support for breakout cables (4×10G).
-
QSFP28: Supports 100 Gbps and can break out to 4×25G. Common in modern data centers and core networks.
-
QSFP-DD (Double Density): Supports up to 400 Gbps. Designed for very high-capacity networks and future scalability.
-
CFP and CFP2: Larger form factors designed for high-speed (100G+) long-haul and metro networks, though less commonly used now.
-
DWDM Modules: Allow dense wavelength-division multiplexing to send multiple signals over one fiber, useful in long-distance and ISP-level networks.
Specifications of Different types of Cisco Fiber Optic Module:
1. SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable)
-
Data Rate: Up to 1 Gbps
-
Fiber Type: Multi-mode (MMF) or Single-mode (SMF)
-
Distance:
-
MMF (SFP-SX): Up to 550 m (on OM2), 2 km (on OM3/OM4)
-
SMF (SFP-LX): Up to 10 km
-
-
Wavelengths: SX (850 nm), LX (1310 nm)
-
Use Case: Enterprise access layers, legacy systems, switches, and routers
 2. SFP+ (Enhanced SFP)
2. SFP+ (Enhanced SFP)
-
Data Rate: Up to 10 Gbps
-
Fiber Type: MMF or SMF
-
Distance:
-
SR (MMF): 300 m on OM3, 400 m on OM4
-
LR (SMF): 10 km
-
ER (SMF): 40 km
-
ZR (SMF): 80 km
-
-
Wavelengths: 850 nm (SR), 1310 nm (LR), 1550 nm (ER/ZR)
-
Use Case: Data center links, distribution layers, server connectivity

3. QSFP (Quad SFP)
-
Data Rate: 40 Gbps (4 × 10 Gbps lanes)
-
Fiber Type: MMF or SMF
-
Distance:
-
SR4 (MMF): 100 m (OM3), 150 m (OM4)
-
LR4 (SMF): 10 km
-
-
Wavelengths: 850 nm (SR4), 1310 nm (LR4)
-
Use Case: Aggregation, spine-leaf topology, high-speed links

4. QSFP+
-
Data Rate: 40 Gbps
-
Fiber Type: MMF or SMF
-
Distance:
-
Similar to QSFP (SR4 and LR4)
-
-
Special Feature: Breakout capability (e.g., 4×10G to 4 SFP+ ports)
-
Use Case: Data centers and high-density switching

5. QSFP28
-
Data Rate: 100 Gbps (4 × 25 Gbps lanes)
-
Fiber Type: MMF or SMF
-
Distance:
-
SR4 (MMF): 70 m (OM3), 100 m (OM4)
-
LR4 (SMF): 10 km
-
ER4 (SMF): 40 km
-
-
Wavelengths: 850 nm (SR4), 1310 nm (LR4), 1550 nm (ER4)
-
Use Case: 100G data center uplinks, aggregation, core network

6. QSFP-DD (Double Density)
-
Data Rate: 200–400 Gbps (8 × 50 Gbps or 8 × 100 Gbps lanes)
-
Fiber Type: MMF or SMF
-
Distance:
-
SR8: ~100 m (MMF)
-
DR4: ~500 m (SMF)
-
FR4: ~2 km (SMF)
-
LR4: ~10 km (SMF)
-
-
Use Case: Hyperscale data centers, cloud computing, future-proofing core networks

7. CFP / CFP2
-
Data Rate: 100 Gbps and higher (CFP2 up to 200 Gbps)
-
Fiber Type: SMF
-
Distance: Up to 10–100 km (depending on optical variant)
-
Wavelength: 1310 nm, 1550 nm
-
Use Case: Long-haul transport, metro networks, telecom applications

8. DWDM SFP/SFP+/XFP
-
Data Rate: 1G / 10G / 100G depending on form factor
-
Fiber Type: SMF (using DWDM filters)
-
Distance: Up to 80 km or more with amplification
-
Wavelength: Multiple (ITU grid: 1525–1565 nm)
-
Use Case: ISP networks, carrier backhaul, wavelength-division multiplexing systems
How Cisco Fiber Optic Modules work?
Cisco fiber optic modules operate by converting electrical signals from networking devices (like switches and routers) into optical signals, which are then transmitted through fiber optic cables. At the receiving end, another module converts the optical signal back into an electrical signal for the receiving device to process.
This conversion enables high-speed, long-distance communication with minimal signal loss. These modules are hot-swappable, meaning you can insert or replace them without shutting down the device. Each module includes a transmitter (TX) and a receiver (RX) with specific lasers and photodiodes matched to the fiber type and required distance.
The operation also involves auto-negotiation, error checking, and management functions through standardized interfaces like DOM (Digital Optical Monitoring).
- Signal Conversion:
Converts electrical signals to optical signals for transmission, and back to electrical at the receiving end. - Transmitter (TX):
Uses a laser or LED to send data over fiber optic cable (wavelength depends on module type). - Receiver (RX):
Uses a photodiode to detect incoming light and convert it back to an electrical signal. - Hot-swappable:
Can be inserted or removed without powering down the switch or router. - Auto-Negotiation:
Communicates with the remote device to match speed and settings. - Digital Optical Monitoring (DOM):
Monitors signal strength, temperature, voltage, and other diagnostics. - Distance Handling:
Uses different wavelengths and power levels to support short or long distances depending on the module type. - Form Factor Matching:
Physically fits into specific ports designed for its type (e.g., SFP, QSFP).
The Most Popular Types of Cisco Fiber Optic Modules:
These models are commonly found in enterprise networks, data centers, and service provider environments due to their reliability and versatility.
SFP (1G):
-
Model: Cisco GLC-SX-MMD
-
Description: 1G SFP, multimode fiber, up to 550 meters, 850 nm
-
Popular because: It’s affordable and widely used for short-range connections in enterprise networks.
SFP+ (10G):
-
Model: Cisco SFP-10G-SR
-
Description: 10G SFP+, multimode fiber, up to 300m (OM3) / 400m (OM4), 850 nm
-
Popular because: Ideal for short-distance 10G links inside data centers.
-
Alternate: Cisco SFP-10G-LR (for long-range, up to 10 km)
QSFP (40G):
-
Model: Cisco QSFP-40G-SR4
-
Description: 40G QSFP, multimode fiber, up to 100–150 meters, MTP connector
-
Popular because: It’s used in high-speed aggregation links in modern networks.
-
Alternate: Cisco QSFP-40G-LR4 (for long-distance 40G links)
QSFP+ (also 40G):
-
Model: Cisco QSFP-40G-CSR4
-
Description: Extended reach over MMF (up to 300m), compatible with QSFP+ ports
-
Popular because: Provides more distance than SR4 while remaining cost-effective.
QSFP28 (100G):
-
Model: Cisco QSFP-100G-SR4-S
-
Description: 100G QSFP28, multimode fiber, 100 meters (OM4)
-
Popular because: Common in core and spine-leaf data center architectures.
-
Alternate: Cisco QSFP-100G-LR4-S (for up to 10 km on SMF)
QSFP-DD (400G):
-
Model: Cisco QSFP-400G-DR4
-
Description: 400G QSFP-DD, single-mode fiber, up to 500 meters
-
Popular because: It’s an industry-standard 400G model for hyperscale data centers.
CFP/CFP2:
-
Model: Cisco CFP-100G-LR4
-
Description: 100G CFP, single-mode, up to 10 km
-
Popular because: It was one of the earliest 100G modules for long-haul and metro networks.
DWDM SFP+:
-
Model: Cisco DWDM-SFP10G-XX.xx
-
Description: 10G DWDM, channel-specific (e.g., 1548.51 nm), supports long distances with amplification
-
Popular because: Used by ISPs and carriers to multiplex many channels on one fiber.
Description Of Popular Models of Cisco Fiber Optic Modules:
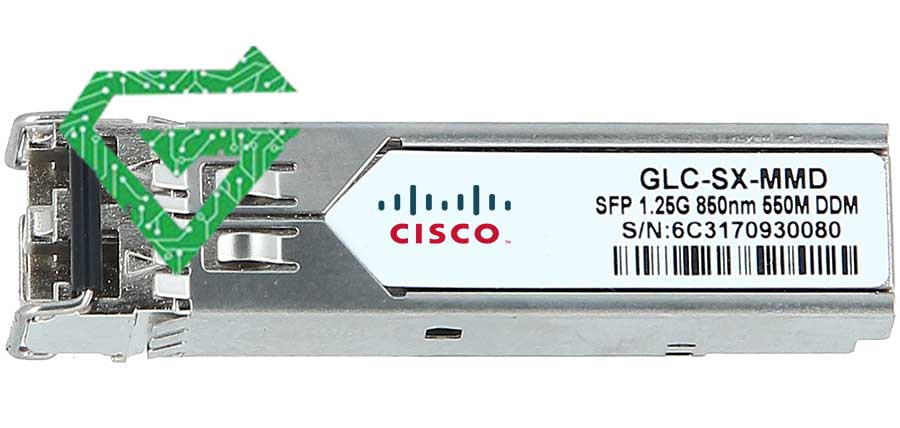
1. Cisco GLC-SX-MMD (SFP – 1G):
The GLC-SX-MMD is a Gigabit Ethernet SFP transceiver designed for short-range optical communication over multimode fiber (MMF). It operates at 850 nm and supports link lengths of up to 550 meters on OM2 and even longer on OM3/OM4 fiber. It features Digital Optical Monitoring (DOM) to monitor signal strength and module health. It’s hot-swappable, compatible with a wide range of Cisco switches, and is widely used in enterprise LAN environments due to its low cost and reliability.

2. Cisco SFP-10G-SR (SFP+ – 10G):
The SFP-10G-SR is a widely used 10 Gigabit SFP+ transceiver for short-range links. It uses 850 nm lasers to transmit over MMF and supports up to 300 meters on OM3 and 400 meters on OM4 fiber. It’s hot-pluggable, supports DOM, and is compliant with the IEEE 802.3ae 10GBASE-SR standard. It’s ideal for data center environments where short intra-rack or inter-rack connections are required.
3. Cisco QSFP-40G-SR4 (QSFP – 40G):
The QSFP-40G-SR4 is a 40 Gigabit transceiver module designed for high-performance data centers. It transmits four parallel lanes of 10G each, using MTP/MPO connectors and 850 nm lasers over MMF. It supports distances up to 100 meters (OM3) or 150 meters (OM4). It is hot-swappable, supports DOM, and complies with the QSFP MSA and IEEE 802.3ba 40GBASE-SR4 standard. It’s commonly used in aggregation and spine-leaf topologies.

4. Cisco QSFP-40G-CSR4 (QSFP+ – 40G):
The QSFP-40G-CSR4 is a 40G module like SR4 but designed for extended reach. It can go up to 300 meters on OM3 and 400 meters on OM4, making it suitable for slightly larger data center environments. It uses the same MTP/MPO connector and supports 4×10G breakout to individual SFP+ ports. This is especially useful for flexible cabling and high-density server-to-switch connections.

5. Cisco QSFP-100G-SR4-S (QSFP28 – 100G):
The QSFP-100G-SR4-S is a 100 Gigabit module that uses 4 lanes of 25G each over MMF. It operates at 850 nm and supports distances up to 70 meters (OM3) or 100 meters (OM4) using MTP/MPO connectors. It complies with the 100GBASE-SR4 standard and is used primarily for core switching, spine-leaf architecture, and high-speed uplinksin modern data centers. Its compact design and short reach make it cost-effective and efficient.
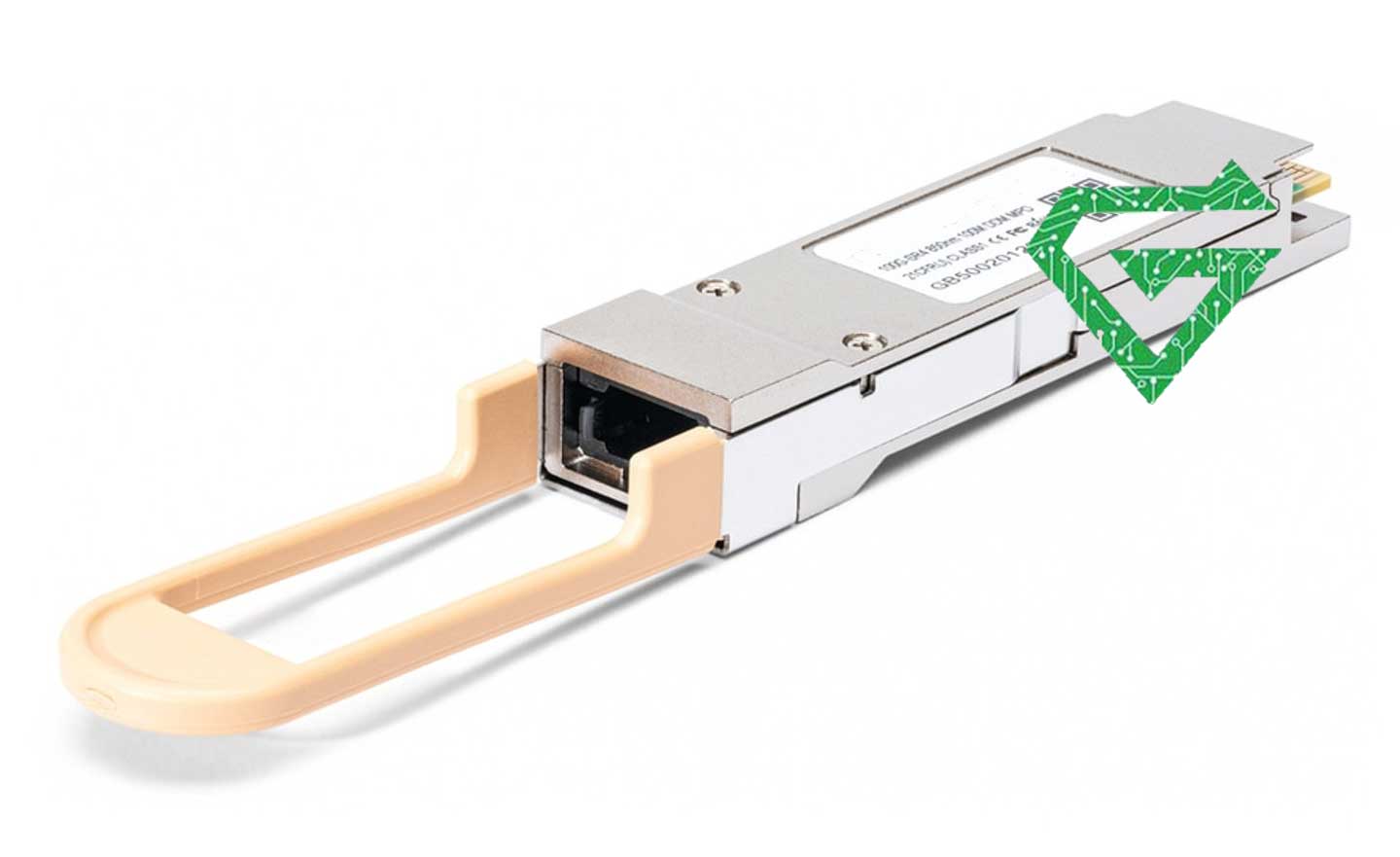

6. Cisco QSFP-400G-DR4 (QSFP-DD – 400G):
The QSFP-400G-DR4 is a high-performance 400G transceiver designed for next-generation data centers. It supports 4×100G lanes over single-mode fiber (SMF) using 1310 nm lasers and MPO-12 APC connectors. It reaches up to 500 meters, making it ideal for high-speed interconnects within large data centers. It is hot-pluggable, supports Digital Monitoring, and complies with the 400GBASE-DR4 standard. It is a future-ready solution for hyperscale environments.
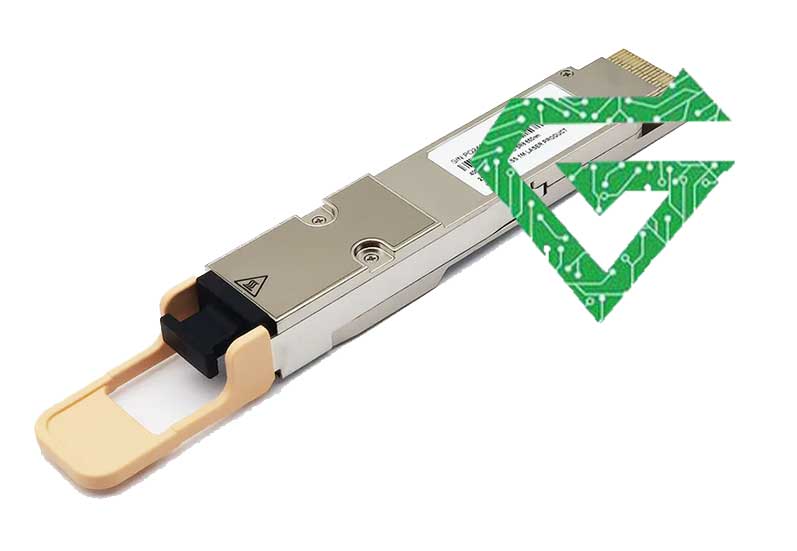

7. Cisco CFP-100G-LR4 (CFP – 100G):
The CFP-100G-LR4 is a 100 Gigabit module that supports long-haul transmission over single-mode fiber at distances up to 10 km using 1310 nm wavelength. It transmits data over 4×25G lanes multiplexed together. It is larger in size than QSFP modules and is commonly found in telecom, metro, and carrier-grade networks. It supports OTN (Optical Transport Network) and full DOM functionality for diagnostics.
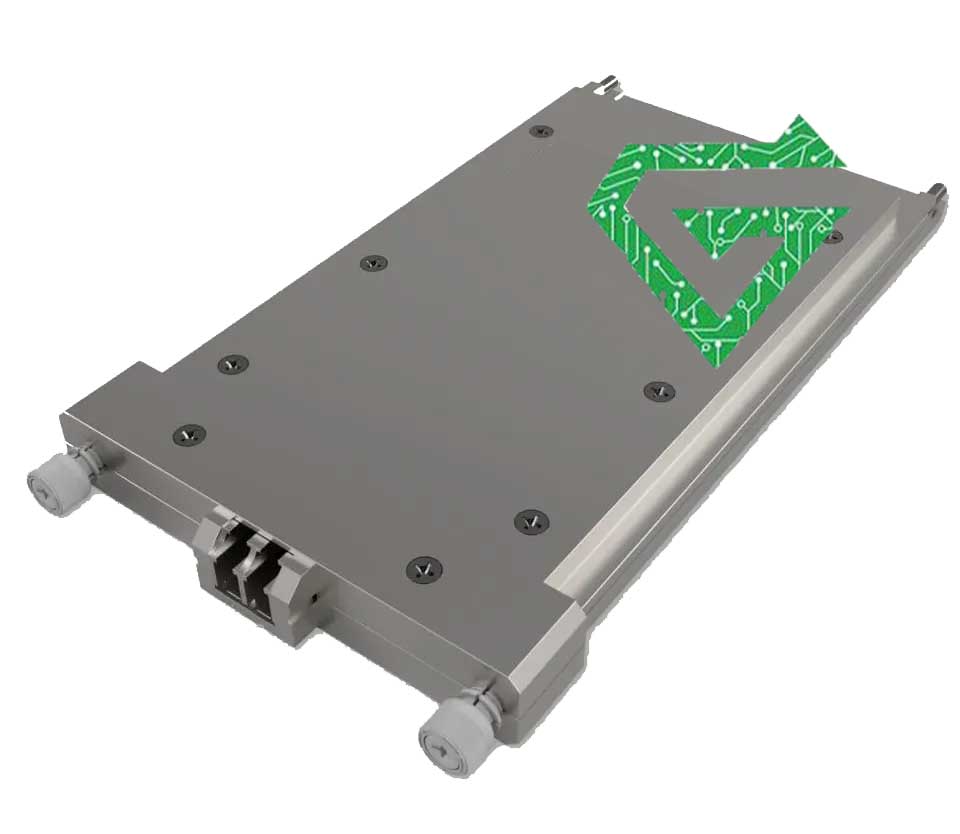

8. Cisco DWDM-SFP10G-XX.xx (DWDM SFP+):
The DWDM-SFP10G is a 10G Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing transceiver for long-distance communication. It operates over single-mode fiber using one of 80+ ITU-T C-band wavelengths (e.g., 1548.51 nm) and supports distances up to 80 km or more with the help of amplifiers and dispersion compensators. This model is critical in carrier networks, ISPs, and optical transport systems, allowing multiple channels over a single fiber pair to maximize bandwidth.

Conclusion:
Cisco fiber optic modules come in various types and models, each designed to meet specific network needs in terms of speed, distance, and application. From the basic GLC-SX-MMD SFP for 1G short-range access to advanced QSFP-DD and CFP modules supporting 100G to 400G for core and long-haul links, Cisco offers a scalable range of transceivers.
Modules like SFP-10G-SR and QSFP-40G-SR4 are widely used in data centers for high-speed, short-distance connectivity, while QSFP-100G-SR4-S and QSFP-400G-DR4 address modern backbone and spine-leaf architecture needs.
Long-range options such as SFP-10G-LR, CFP-100G-LR4, and DWDM-SFP10G enable service providers and enterprises to build wide-area and multiplexed optical networks. These modules are plug-and-play, hot-swappable, and support features like digital monitoring, making them essential for reliable and flexible network infrastructure.





