What is HP Server Memory
Every server, laptop and computer have memory. Although server memory is just a small part of the overall server system, its importance cannot be underestimated. If the server memory is not working properly, the server system may experience problems like system freezes or blue screen, which will cause great damage to companies.
Without memory hardware, such as server RAM or ECC memory, the system cannot even boot. Therefore, it’s necessary to have a basic understanding of server memory. In this article, we will talk about server RAM and especially HP server memory. Follow us to end.
What is HP Server Memory:
Your devices get higher performance and more power saving and even efficiency with HP Ram Server. HP-qualified memory, built to work with HP ProLiant servers and capable of enhanced support through HP Active Health System. HP Qualified Option mean every original HP DIMM has been through our rigorous qualification process, which extends beyond standard industry practice to help ensure compatibility, performance, and reliability.
Designed for energy efficiency, HPE Server Memory helps lower overall server power consumption, therefore reducing server operating costs, while ensuring that performance and reliability are not compromised. Server memory is Random Access Memory (RAM) which processes data from HDDs to the CPU. As a form of volatile memory, when server memory is powered off it loses all its held information. One way to think about this is that your RAM modules are the short-term memory, and your HDDs are the long-term memory.
HPE RAM Server is tested in extreme operating environments to ensure reliability and maximum system uptime. RAM memory processes data from the hard drive or solid state drive, stores this data and instructions, and enables the central processing unit (CPU) to access it. Without memory, your system wouldn’t be able to carry out any tasks.
Most servers and workstations come with just enough factory standard memory. However, for most businesses “just enough” won’t get the job done. Upgrading the memory in your HP networking product will ensure that system processes run smoothly and effectively with no lag, so they can be very necessary for your devices.
Increasing your systems memory capacity is a cost effective way to boost the performance and longevity. Atech.ae has a great variety of quality HP memory kits to fit your budget and your IT needs. All of our memory modules and memory server hard drive such as Hard server and HPE Hard Server have been tested by certified technicians for reliability and you can provide them from Atech.ae, one of the best in network equipment.
What are Buffered RAM and Unbuffered RAM?
Typically, there are two main types of Ram server; buffered RAM and unbuffered RAM. The major difference between these two memories is that buffered memory contains registers between Dynamic Random Access Memory (DARM) modules and memory controller, where unbuffered memory does not.
- Buffered RAM
Buffered memory, also called registered memory, is used to reduce electrical load on the server memory controller. Besides, buffered RAM is usually used for servers and other high-end systems that need a stable operating environment, because it has high stability in stored data.
The biggest advantage of buffered RAM is the buffer, which can receive information directly from the CPU, thus reducing actual physical read and write times. Basically, there are three types of buffered -memory are registered memory (RDIMM), local reduced memory (LRDIMM) and fully buffered memory (FBDIMM).
–RDIMM: Unlike unbuffered memory, registered memory contains registers on the DIMM to buffer command signals between DRAMs and the memory controller. This allows the use of up to three dual-rank DIMMs per memory channel, thus increasing the amount of memory that the server can support.
–LRDIMM: As a new version of buffered memory, LR-DIMM provides large overall maximum memory capacities since it makes use of memory buffers to integrate the electrical loads on the ranks of the LR-DIMMs into a single electrical load. However, it also generates more power and has lower latency compared to R-DIMM.
–FBDIMM: FB-DIMM is an older version of buffered memory, which is also a RAM production technology. It is used to improve the speed, stability and compatibility of server memory to the most extent. FB-DIMMs and LR-DIMMs are not compatible with R-DIMMs, and they are used to reduce the load on the memory bus by the memory modules.
- Unbuffered RAM
In unbuffered memory, the CPU will directly access the memory controller since there is no register between DARM modules and memory controller. Different from buffered memory, it will generate more electrical load on the memory controller.
Unbuffered RAM is commonly used for desktops, laptops, etc. Because of its relatively low price. However, it is less stable for systems and stored data.
Read more: What is HP server
Types of Server RAM:
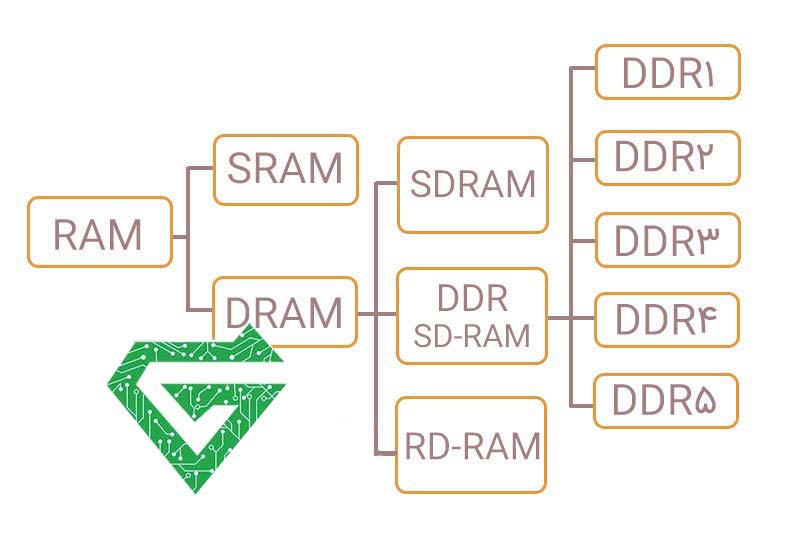
First of all, let’s take a look at the classification of computing memory and Types of Ram server as the following figure shows. There are two basic memory types: static RAM (SRAM) and dynamic RAM (DRAM), which processes data in different ways.
SRAM stores data using the six transistor memory cells while DRAM is made up of two parts: a transistor and a capacitor, which are arranged in an integrated circuit.
- Since the number of transistors determines the capacity, SRAM is limited in storage capacity. On the contrary, it is easier to achieve high storage density and capacity, which enables users to create a large RAM system when using DRAM.
- Due to the fact that SRAM uses a larger number of transistors than DRAM, the construction of SRAM is more complex while DRAM is easier. Therefore, SRAM is more expensive than DRAM.
- However, SRAM has its advantage: It is high speed cash memory and SRAM is much faster than DRAM which has to be refreshed once in a while.
The design of DRAM is aimed at overcoming the disadvantages of SRAM. Though reducing the memory elements helps with the reduction in cost and increase of storage area but makes DRAM slower, most RAMs we meet today in general usage are DRAM.
Read more: What is HPE GreenLake?
DRAM Classification:
With the explosive increase of 5G, cloud computing, IoT and other applications requiring massive data storage, the need for DRAM is expected to grow rapidly. In terms of the technology applied, DRAM can be classified into three types: SDRAM, ROADM and DDR SDRAM. Do not mix up SRAM and SDRAM together though they look alike.
- SDRAM and DDR
SDRAM is the abbreviation of Synchronous DRAM because SDRAM is designed to synchronize itself with the timing of CPU Server. The SDRAM chip’s memory speed is synchronized with the CPU clock speed. So that the CPU can perform more instructions at a time.
SDRAM has been in existence for many years and is widely used in computers and other technology. DDR actually is the newer generation of synchronous DRAM, which has variants from DDR1 to DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 and the latest fifth generation of DDR: DDR5. It is also called DDR SDRAM because it has double the data rate of SDRAM.
As time goes by, DDR was superseded by the newer generations but they all operate on the same principle as DDR. Until now, DDR1 and DDR2 are no longer in use but DDR3, DDR4 and DDR5 are still widely used in the market. If you are curious about the difference among these relatively updated DDR formats, you can click DDR3 vs. DDR4 vs. DDR5 for reference.
Now, let’s turn back to the SDRAM and its variant DDR. The following figure comparing SDRAM and DDR will help you know better about them:
| SDRAM | DDR | |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory | Double Data Rate Dynamic Random Access Memory |
| Year of Release | 1997 | 2000 |
| Pins and Notches | 168 pins and 2 notches at connector | 184 pins and 1 notch at connector |
| Transfer Speed | Less speed than DDR | Nearly twice the speed of SDRAM |
| Voltage Requirement | 3.3 Volts | 2.5 Volts (standard) |
| Low Voltage Requirement | 1.8 Volts (low voltage) | |
| Clock Speed | Ranges between 100MHz to 166MHz | Ranges between 133MHz to 200MHz |
| Data Rate | 0.8-1.3 GB/s | 2.1-3.2 GB/s |
| Prefetch Timing | 1ns | 2ns |
- RDRAM
RDRAM is the abbreviation of Rambus DRAM, which was available as an alternative to SDRAM in the past. Due to manufacturing costs and licensing fees, the cost of RDRAM is much higher than SDRAM, generally two to three times the cost of SDRAM. It was found in late 1999 through 2002 and applied to high-end PC systems and servers. Nevertheless, chipsets and motherboards started to shift to DDR after RDRAM, RDRAM is less likely to play a big role in server RAM. Most servers currently use DDR SDRAM, but only a small amount of RDRAM is utilized.
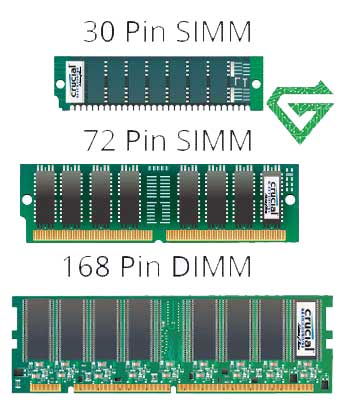
Difference between DIMM & SIMM Memory Module:
In the terms of the appearance that pins installed on DRAM’s sides, Single In-Line Memory Module (SIMM) and Dual In-Line Memory Module (DIMM) are the two different types of DRAM in physical terms. They are different in pin outs, memory capacity and mechanical outline. SIMM has a 32-bit memory bus width, while DIMMs offer double that—64 bit, which support up to 128GB of memory.
DIMM has more pin versions than SIMM, including pins for power and ground connections, while SIMM doesn’t. And DIMM often has a longer length than SIMM because it has pin connections on both sides but SIMM has only one With the RAM walking into the generation of SDRAM and DDR, the memory module type shifts from SIMM to DIMM.
Nowadays most servers today still use DIMM. SIMM is outdated, but it is still used on some older released 32bit servers. Check out the specifications of servers from different server vendors, you will find that many servers support DDR4/DDR5 RAM with 1/2 DIMM per channel. The number of DIMM slots is often connected with the RAM capacity. The more DIMM slots your Motherboard Server has, the more RAM you can install.
What Are Server Memory Technologies?
The reason server RAM outperforms PC RAM is its unique technologies, such as ECC, Chip kill and register, which provide extremely high stability and error correction performance for server memory.
- ECC Memory:
Error Checking and Correcting (ECC) is an error correction technique in computer instructions widely used in various fields. Compared to Parity, an error-checking technology used in ordinary server memory, ECC technology can not only check for errors but also correct them. Due to electrical factors, the data transferred in server memory can not be completely accurate. With ECC memory, the stability and reliability of server systems can be guaranteed.
- Register:
Register is another technology widely used in server RAM. Actually, registers are to the server memory what directories to books. With register, after receiving instructions, the server memory can retrieve the directory first, and then perform read and write operations. By doing so, the working efficiency of server RAM will be greatly increased. What’s more, currently popular register memory is also equipped with ECC technology, so it is also called ECC Registered memory. These two always complement each other.
- Chip kill Memory Technology:
Chip kill memory technology was developed by IBM 20 years ago to solve the shortage of ECC technology in server memory. It is a new ECC memory protection standard. Since ECC cannot correct errors of more than two bits, all bits of data will be likely to get lost, resulting in system crashes.
However, data can be written to multiple DIMM memory chips via Chip kill technology, which means that if any one of the chips fails, it affects a certain bit of a data byte, rather than the normal operation of servers. In addition, with Chip kill memory technology, server memory can check and fix up to 4 bad data bits at the same time, further improving server usability.
- Memory Mirroring:
Memory mirroring is a technique that divides server memory into two independent channels. Typically, one channel replicates another for redundancy.
For instance, if DIMM fails, the entire server system won’t get affected, because the memory controller is immediately moved to another channel. Therefore, with memory mirroring, a higher level of memory reliability and consolidation can be achieved. Besides, it also provides comprehensive protection against single bit and multiple bit errors.
- Memory Protection:
Just as its name shows, memory protection is a strategy that controls the amount of memory access rights on a computer. The main purpose of it is to prevent applications from taking advantage of memory that systems have not allocated to, which can avoid damage or data loss to some extent.
Similar to the hot backup of hard disks, memory protection technology can use the spare bits to retrieve data when the DIMM fails, thus ensuring the smooth operation of server. It can also correct up to 4 consecutive bit errors in each pair of DIMMs.
Read more: What is Cisco network module
What Server Memory Technologies can help you in key terms?
There are numbers of different variations you can have within memory, including speed, capacity and rank. Here are explanations for each element of server RAM.
- Ranks and bandwidth:
A good way to think about server memory ranks is as lanes, and the bandwidth as cars. More ranks means that more data can be transferred to the CPU. More bandwidth means that there are more units (cars) to carry this data. Having the optimum rank for your server ensures that you will not experience any bottlenecking, and server performance will be as smooth as possible. Speed is always measured in megahertz (MHz), and bandwidth is millions of transfers per second (MT/s).
When server memory fails, data loss and system faults are common, which leads to downtime and inefficiency. If you’re looking to protect your system against bottlenecking or increase server memory performance, upgrading your server memory is the easiest and most affordable way.
- ECC-Error Correcting Code:
If your server memory module has ECC, it means that the code can detect any minor faults in your server and correct them. This decreases the chance for downtime or crashes, and keeps your system running smoothly. In other words, it’s a form of memory protection.
- DDR-Double Data Rate:
From the latest DDR technology (DDR4) to previous generations (DDR3, DDR2), an extensive range of server memory modules in stock including HPE, Samsung, Dell and Orptial. When using the most appropriate DDR technology, speed and rank for your specific system, server RAM ensures that your data center output is maximized.
The generation of your RAM and motherboard need to be compatible. For example, DDR3 memory can’t be used with a motherboard with DDR4 DIMM slots. This is because the older generations haven’t been built to support the functionality of newer generations
- Motherboard:
RAM memory can easily be installed by inserting it into an empty DIMM slot on your motherboard. Some motherboards only have 2 DIMM slots, so be aware how many memories sticks your motherboard can hold before you make your purchase.
- Capacity:
Capacity describes the amount of RAM, measured in gigabytes (GBs), present in your modules. 16GB and 32GB are common capacities of server memory. In terms of size, for high-end workstations 16GB minimum is probably best, whereas for more budget friendly home set ups, 8GB should about do. Looking at servers, 16GB and 32GB are common capacities of server memory, although they can support up to 6TB for 2933 MT/s DDR4.
- Latency:
Latency describes the access time. A lower latency means you will have a quicker server.
Read more: What is HP Server Hard Drive
A glance at memory of desktop and laptop:
Desktop memory isn’t too different to RAM memory. The main difference is that server RAM supports ECC, whereas most desktop, PC and laptop system boards do not have that option enabled. Instead, most desktop computers use non-parity DIMMs which tends to be unbuffered and non-ECC.
Laptops use SODIMMs, which stands for Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module. As it is around half the size of server memory, SODIMM is perfect for laptops and notebooks, which do not have much space. Even though they are much smaller than regular server memory modules, they pack almost the same amount of system performance.
How to Choose the Best Server Memory?
There are a lot of factors that need to be considered when choosing server memory, and they all depend on your use case. It is crucial to assess all the points mentioned above surrounding your project to make the right decision. The choice of server memory – both amount and module types – goes together with other components that interact with RAM, such as server memory ranks, ECC, DDR, motherboard, server CPU, and server storage, so be sure to check that all components are compatible.
If you are looking to run a dedicated server, you are going to need a decent amount of server RAM to ensure the server is capable of handling the load. Atech.ae provides a variety of server memory options, users can purchase or customize servers such as HPE server according to project needs, ensuring the perfect match of components.
Conclusion:
To sum up, server memory plays an important role in server systems. Upgrading server RAM can provide the server system with higher stability and efficiency. Basically, buffered memory and unbuffered memory are two main types of server memory. Moreover, RAM Server can realize better performance by using technologies like ECC memory, register, Chip kill memory, etc.





